I.INTRODUCTION
The exploration of unknown, undefined, or impossible data is considered as one of the most crucial tasks for past years [1]. The reason is these types of data sets and its characterization exist beyond the beyond true, false, and uncertain regions [2]. It is totally based on human Turiyam cognition rather than some defined algebra [3]. To achieve this goal, the concept of Turiyam set is introduced in Int’l Conference on Operations Research and Applications (ORA 2021) held at Guilin, China [4], which is later applied at several fields [5]. The problem arises when the data sets are undefined, impossible, or unknown or beyond Euclidean [6–11]. The exploration of these types of data sets is based on human cognition, and its consciousness to characterize them in true (t), false (f), uncertain (i), or undefined or Turiyam regions (l), independently [12,13]. The algebra of Turiyam set provides a way to represent these types of data sets more precisely for knowledge processing tasks [14,15]. The problem arises while exploration of these types of data sets [16–19] and its visualization [20–22]. It is indeed a requirement for precise representation of human quantum cognition [23]. Even the car driving is totally based on human Turiyam cognition to control the accident rather than green (true), red (false), or yellow (uncertain) regions [24]. Same time searching of any element at online website is based on Turiyam awareness rather than indexing [25]. Dealing these types of data sets requires new mathematical algebra for precise representation and visualization for better understanding. To accomplish this task, one of the methods is proposed in this paper with some examples.
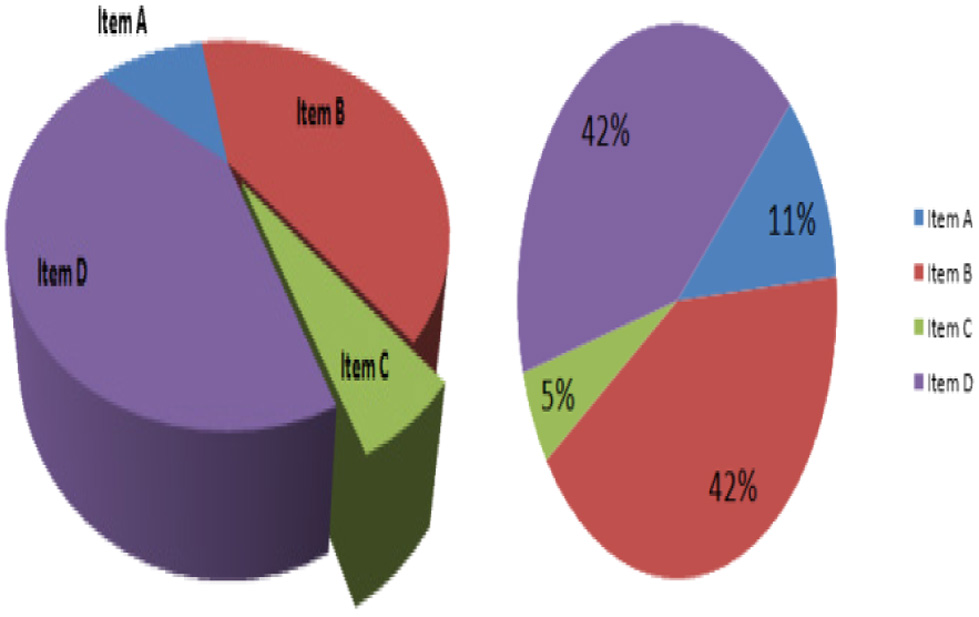
One of the suitable examples of Turiyam data sets is Indian voting system where people support a party (t), reject the party (f), absent or unable to reach at booth (i), and the last is NOTA (i.e., l). NOTA are the votes where people choose that none of the politicians are eligible. It is totally awareness of voting as compared to true and false, which can be called as Turiyam as shown in Fig. 1. The people who refused to vote can be investigated as (1-t-f-i-l). It is called Turiyam or four-dimension cognition as discussed by Nāgārjuna shown in Fig. 2.
 Fig. 1. The four valued characterization of voting.
Fig. 1. The four valued characterization of voting.
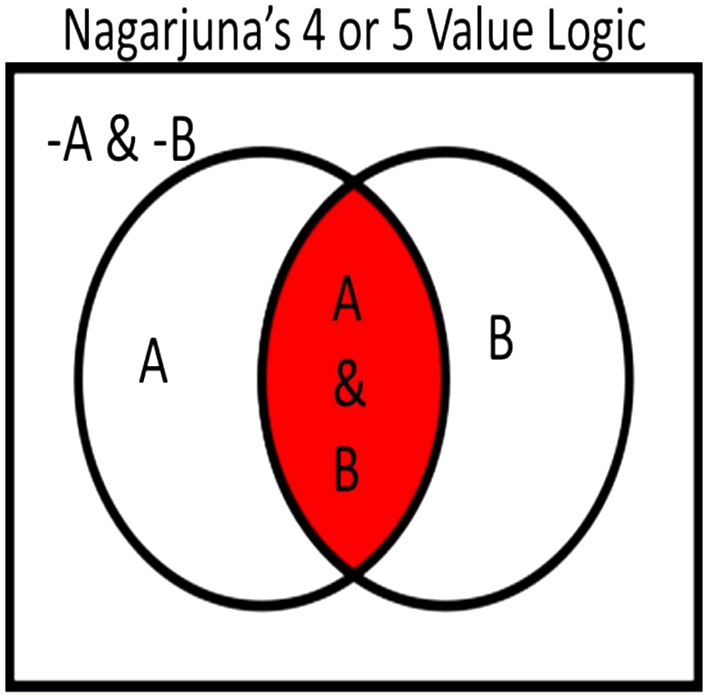 Fig. 2. The four valued logic defined by Nāgārjuna.
Fig. 2. The four valued logic defined by Nāgārjuna.
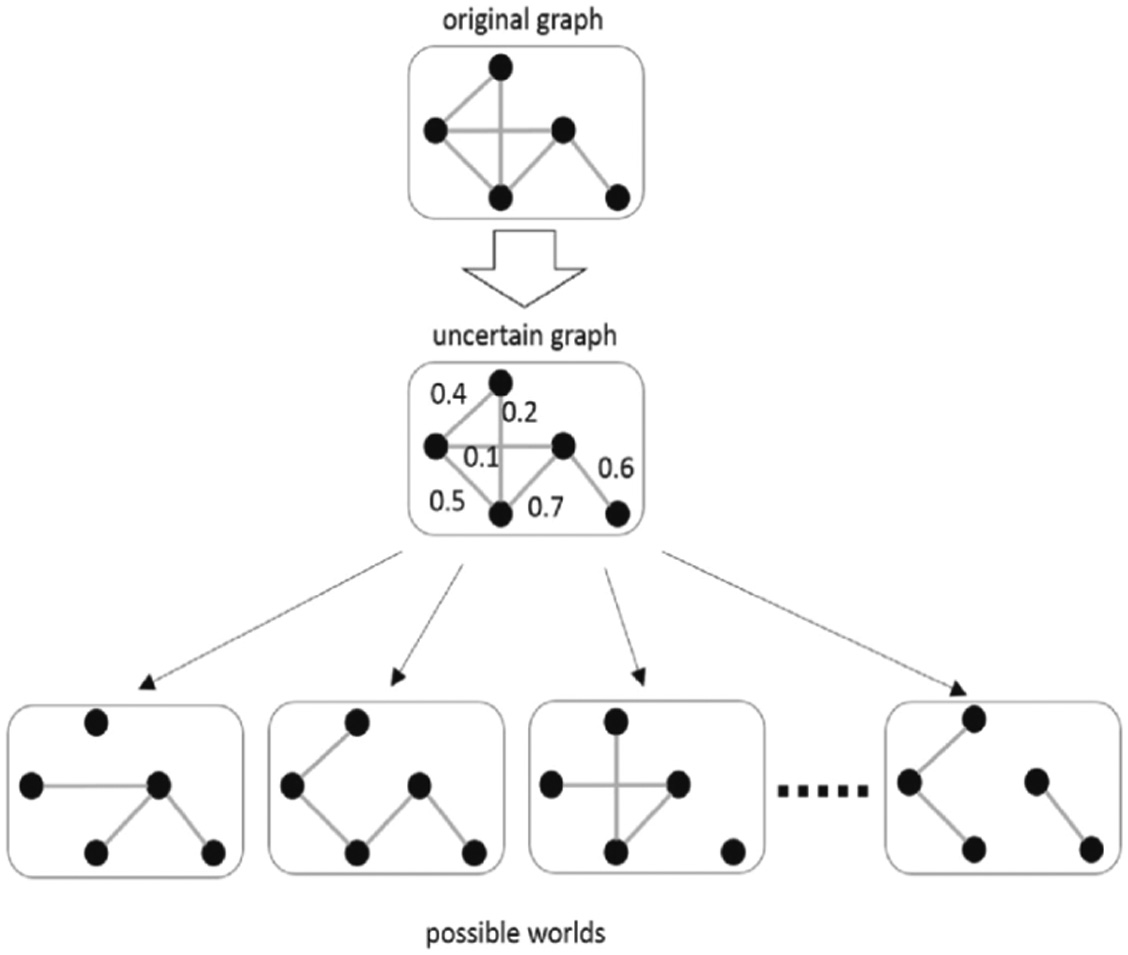
The precise visualization of these types of data sets as vertex and edges of graph is most crucial tasks. The reason is it creates the following issues:
- (i)The graph (V, E) where vertex and edges are known or true graph,
- (ii)The graph (V, E) where vertex is misleading or edges also. It can be considered as Misleading or False graph (f),
- (iii)The graph (V, E) where vertex is known, but edges is unknown. It is like partial graph, dynamic graph where deciding next edge is issues. It can be considered as uncertain graph (i),
- (iv)The graph (V, E) where the vertex and edges are unknown or nothing. The characterization of these types of unknown or undefined graph based on possible vertex combination and its exploration are crucial tasks. It is totally based on Turiyam cognition of any expert. It can be characterized as Turiyam vertex (t, i, f, l) and edges.
The exploration of these types of graphs is more difficult than space time tradeoff. To resolve this issue, one of the methods is discussed in this paper. One of the advantages of the proposed method is that it provides the characterization in true, false, and uncertain regions based on computed subset. It will be easier to understand for further processing.
Other parts of the paper are structured as follows: Section II provides brief background about Turiyam set and its visualization. Section III provides the proposed method to characterize the unknown data, unknown graph in Turiyam, or fourth dimension with its illustration in Section IV. Section V contains conclusions followed by acknowledgements and references.
II.DATA WITH TURIYAM SET
This section provides basic of Turiyam set for data representation:
Definition 1 (Turiyam Set) [4]: It contain 4-tuple: truth (t), indeterminacy (I), falsity (f), and liberalization (l). Each of the dimensions is independent to each other as: The Turiyam value 0 represents the universal neutral values, −4 represents universal false cases, and +4 represents the universal truth cases, i.e., . It means this set contains a true, a false, an indeterminacy membership values, and a liberalization values, which can be characterized independently as where 4+. This set can be scaled within [0, 1] in case of dependent case. It can be represented via four coordinates as shown in Fig. 3.
Definition 2 (Intersection of Turiyam) [5]: The intersection of Turiyam set T1 and T2 can be computed as follows:
It will be helpful in finding the maximum common opinion in two intellectuals and their conversations.Definition 3 (Union of Turiyam): The union of Turiyam set T1 and T2 can be computed as follows:
It will be helpful in finding that two intellectual of different era or space are once agree on a given thought.Definition 4 (Complement of Turiyam) [3]: The complement of Turiyam set can be computed as follows:
It will be helpful in finding the refusal degree of two intellectual based on given thought. It means the complements of Turiyam is independent and provide maximum values of nonrefusal.It can be observed that the Turiyam set provides a way to deal with unknown, impossible, and undefined objects based on human consciousness. However, to characterize them for decision-making process and represent them mathematically is a difficult task [6]. To achieve this goal, a method is proposed in the next section.
III.THE PROPOSED METHOD
In this section, a method is proposed to characterize the unknown data sets and its visualization:
- Step 1. Let us suppose any data set (X) that contain n number of elements. The data (X) can be represented as vertex.
- Step 2. Compute its subset, i.e., 2n and characterize them in fourth dimension.
- Step 3. The subset is known 2k. It means that the vertex is known and its edges are also known. It can be characterized as known graph (V, E), where vertex and edges information is efficiently constructed as shown in Fig. 4.
- Step 4. The subset is known 2m, but data are represented in wrong ways. It is like distorted representation rather than proper scaling. It can be characterized as misleading graph (V, E), where vertex and edges are poorly constructed as shown in Fig. 5.
- Step 5. The subset is uncertain or dynamic in (2n-2k) which changes based on its exploration. It can be called as partial graph where someone do not know the next edges after the given vertex. It can be called as partial graph (V, E) where vertex and edges are constructed based on defined membership as shown in Fig. 6. In this case, edges are not unknown fully.
- Step 6. The last case when nothing is known, i.e. (t, i, f, l). The vertex and edges all are unknown. The expert explore based on his Turiyam cognition either in Breadth First search or Depth First Search manner is shown in Fig. 7.
- Step 7. The obtained data can be represented via fourth dimension as (1,1,1,1), (1,1,−1,1), (1,1,−1,−1), and (1,1,1,−1) and are shown in Fig. 8.
- Step 8. The data can be traversed or characterized via four axis as Up-Down or length (x), Left-Right or width (y), Back-Forth or height (z), and Trench or Turiyam (w) as shown in Fig. 9.
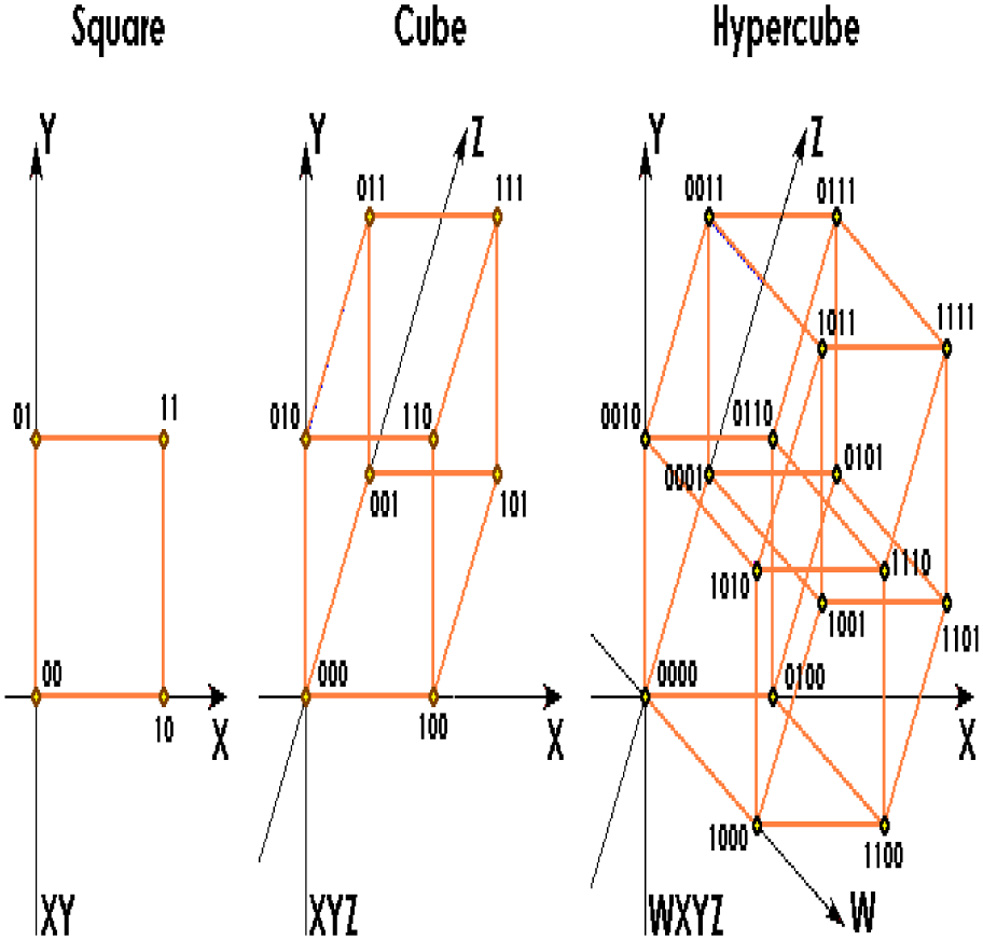 Fig. 4. The four-dimensional data representation and its evolution.
Fig. 4. The four-dimensional data representation and its evolution.
 Fig. 8. The four-dimensional data characterization and its representation.
Fig. 8. The four-dimensional data characterization and its representation.
 Fig. 9. The three-dimensional data visualization and its traversal in fourth dimension.
Fig. 9. The three-dimensional data visualization and its traversal in fourth dimension.
Complexity: The time complexity to explore the unknown data sets in true (t), false (f), uncertain (i), or Turiyam regions (l) depends on known and unknown subsets. It may take maximum O(2nlogn) time as explored vertex is not traversed again. In this case, uncertainty can be controlled. However, its exploration is one of the crucial tasks for the researchers.
A.THE PROPOSED METHOD FOR CHARACTERIZATION OF TURIYAM GEOMETRY
In this section, a method is proposed to explore the unknown, undefined, or four-dimensional data and its characterization via a defined Turiyam Geometry as follows:
- Step 1. Let us suppose the data sets (X) that cannot be represented via Euclidean (t), Non-Euclidean (f), or its Hybrid Geometry (i).
- Step 2. The Turiyam geometry data can be characterized via a Turiyam operator as where .
- Step 3. It means these type of data are not a Euclidean (t), or not Non-Euclidean (f) or not hybrid (i). It is undefined, unknown, or impossible objects that can be characterized based on human consciousness called as Turiyam.
- Step 4. The data can be characterized as follows:
- (i)Let us suppose, non-Euclidean geometry, then Turiyam Operator provides a new element in Non-Euclidean space, i.e., true (1, 0, 0, 1).
- (ii)Let us suppose, non-Euclidean geometry then provides a new element that does not exists in the Non-Euclidean geometry, i.e., false region (0, 0, 1, 1).
- (iii)Let us suppose that non-Euclidean geometry provides a new element which is uncertain that Euclidean or Non-Euclidean. This type of element may be in hybrid or saddle space to define its quantum state as indeterminacy (0, 1, 0, 1).
- (iv)Let us suppose that non-Euclidean geometry provide a new element which is undefined, unknown, and impossible or nothing. It can be characterized as Turiyam Geometry (t, i, f, l).
- Step 5. This type of element can be represented via Turiyam or fourth dimension. The Up-Down or length (x), Left-Right or width (y), Back-Forth or height (z), and Trench or Turiyam (w). These can be written using the vertices of square (1,1,1,1), (1,1,−1,1), (1,1, −1,−1), and (1,1,1,−1).
- Step 6. This vertex can be visualized using Turiyam Graph (V, E) where V represents Turiyam vertex and E represents Hyper edge. It means one edge can cover more vertex for characterization of unknown, undefined, or impossible data as Turiyam. It can be analyzed via intersection and union for pattern analysis:
- Step 7. In case the data cannot be characterized, then its complement can be defined to analyze via Anti-Turiyam:
Complexity: The time complexity to characterize the Turiyam Geometrical data and its graphical visualization may take O(n4) time complexity for true (t), false (f), uncertain (i), or undefined (l) regions. In the next section, another method is proposed to characterize the undefined, impossible, and unknown objects using complement operator.
IV.ILLUSTRATIONS
In this section, some examples of unknown objects, impossible objects, and human cognition characterization based on the proposed method are shown for further improvement.
Example 1. (COVID data set) [5]: The Turiyam set solves the above problem as follows:
- (a)The patients got recovered from COVID-19 can be considered as truth membership values (t),
- (b)The patient still active as COVID-19 can be considered as indeterminant (i),
- (c)The patients may be died due to COVID-19 can be considered as false (f),
- (d)The patient who got vaccinated and watching all these three regions can be called as Turiyam dimensions (l). The defining vaccination is totally unknown as vaccinated people also get COVID or may die. It can be explored based on defined subset of symptoms.
In this way, the Turiyam set provides a way to find those patients who has not affected till now by COVID19 can be found as 1-(t+i+f+l). This is one of the major advantages of the Turiyam set while dealing with medical data set. Hence, COVID data sets and its visualization can be done via Turiyam graph.
Example 2. (Chimera) [6]: This type of object exists due to multiple composition of several genotypes via sexual activity by different animal, animal with human as shown in Fig. 10. This type of images called as Chimera can be characterized based on attributes of image and human cognition that it is men, not men, both or nothing. It can be characterized as follows:Figure 10 contains two animals Lion and Goat where four subsets exist as given below:
- (i)The vertex is {Lion, Lion} and all of its connected images (i.e., symbolic edges) contain properties of Lion. It means the given image is characterized as True regions as Lion (1, 0, 0, 0).
- (ii)The vertex is {Goat, Goat} and all of its connected images (i.e. symbolic edges) contain properties of Goat. It means the given image is characterized as False regions as Goat (0, 0, 1, 0).
- (iii)The vertex is Hybrid {Lion, Goat} or {Goat, Lion}, and all of its connected images (i.e., symbolic edges) and exploration are crucial. The reason is parts of Lion will be connected with Lion and Goat with Goat as mutually exclusive. It means the given graph is uncertain or misleading. It can be represented via membership 50 percent Lion and 50 percent Goat as uncertain graph (0.5, 1, 0.5, 0).
- (iv)The last is nothing is known. None of the vertex can be characterized as specially either as Lion or Goat, independently. It is totally based on human cognition and its experience while exploring the characteristic of animal. This will be characterized as Turiyam as (t, i, f, l).
 Fig. 10. The chimera undefined animal.
Fig. 10. The chimera undefined animal.
Example 3. (Conflict Analysis) [3]:The precise analysis of conflict or cold war among USA and Russia is totally beyond the win, draw, or loss. Let us suppose that the conflict analysis or cold war among USA and Russia is totally beyond the win, draw, or loss. It is totally based on the conduit metaphor of USA and Russia, which depends on 15 members of United Nation Security Council, i.e., 215 subset.Let us suppose k-number of countries are present to vote for Russia and USA conflicts, i.e., 2k subset where k≤15.
- (i)True graph (Vr, Er): A set of countries that support Russia (Sr) can be characterized as true regions. These countries (V) and their relationships (E) are known to everyone. These countries and their graph can be explored in precise way for better understanding.
- (ii)False or Misleading graph (Vu, Eu): A set of countries supporting the USA can be characterized as false regions (Su). These countries and their relationship with the USA can always be easily drawn. However, they just mislead Russia to show the affection.
- (iii)Uncertain graph (Vi, Ei): A set of countries supports Russia or USA based on their metaphor. These types of countries and their vote are uncertain and can be characterized as (2k -Sr). These countries and their relationship with Russia or USA can be defined based on membership values rather than known or misleading graph. They can change their support any time based on their conduit metaphor.
- (iv)Turiyam graph (t, i, f, l): The fourth case is some countries like India or China choose nothing as per their interest to fulfill their hidden agenda. It is not uncertain vote. It is totally based on human cognition but unknown that which agenda is fixed. Everyone knows that due to choosing nothing or Absent India supports Russia. However, no one can define the conduit metaphor behind it. This type of unknown data can be characterized as (215-2k). These countries support Russia as superconscious rather than voting to fulfill their undefined conduit metaphor. These types of data and its pattern can be characterized using four-dimensional data sets and its graph.
Example 4. (Journal Investigation) [4, 5, 24]: The investigations of the journal are based on human or expert cognition, which is based on past experiences. It can be characterized as follows:
- (i)Relevant Journal (1, 0, 0, 1): You aware that some set of researchers whose current research domain is closed with you. Their work is almost relevant to you. These researchers publishes their papers in the given journal can be characterized as true journal for submission of your research work.
- (ii)Irrelevant Journal (0, 0, 1, 1): You aware that some set of researchers whose work is different than your current domain. Those researchers who publish their irrelevant or any work in the connected journal where someone known is in Editorial.
- (iii)Uncertain Journal (0, 1, 0, 0): These journals publishes the papers based on uncertainty or interdisciplinary. The domain of these journals revises from time to time. It is uncertain that some time they publish relevant to your work which changes after some time. This type of journal can be characterized based on membership values. How many papers they published relevant to your areas and irrelevant to your areas or may be other areas. It can be characterized as uncertain journal.
- (iv)Turiyam Journal (t, i, f, l): This is the case when the author considers the journal based on his/her awareness rather than indexing. None of the journals is good or bad and they are just publishers. Work need to be appreciated rather than the journal. It is superconscious awareness that the author knows journal and indexing are nothing. It is just a platform to share the knowledge. The researchers came to know that some of the ranked journal papers are published via biasness and connection, biasing or may be in manipulated way. There are many papers written in conference, open access, or nonindexed journals are also good. This awareness to characterize the work relevant to your research areas rather than the journal is called Turiyam cognition.
- (v)Logic Gate [6]: The four valued logic exists in digital circuits also as 1, 0, Z, and X. The 1 and 0 represent true and false, Z stands for high impedance, whereas X represents do not care conditions. It is also used for data transmission in controller area network as False, True, Error Condition, and Not installed. The Error Condition means that there is a technical problem obstructing the data acquisition. The last one is Not installed which is used for a feature that does not exist. These types of features or data transmission should be disregarded for logical calculation.
- (vi)Reviewer comment characterization: The reviewer comments can also be characterized in fourth dimension using human cognition, which are as follows:
- (i)Relevant Comment (1, 0, 0, 1): You aware that the reviewer comment is relevant to improve the given work.
- (ii)Irrelevant-comment (0, 0, 1, 1): You aware that one of the reviewer comment is irrelevant and create conflict of interest.
- (iii)Uncertain Comment (0, 1, 0, 0): These are the comments that is uncertain. You need to revise and search the answer. These are the comments where reviewer writes both true and false comment to delay the paper.
- (iv)Turiyam comment (t, i, f, l): This is the case when author consider the reviewer comment as nothing. The author knows that the comment is nothing but still consider for the journal acceptance. These can be characterized as reviewer is manipulating or fixing his/her agenda. The reviewer comment is undefined or unknown or misleads the subject. In this case, the editor or expert take decision to accept or reject the paper based on his/her consciousness. Finally, the refusal to resubmit the paper decision can also be written as (1-t-i-f-l).
- (vii)Turiyam Communication: The communications with human to human or machine can be characterized in fourth dimension as follows:
- (i)True Communications (1, 0, 0, 1): You are aware that you are communicating with human. It means these types of data communications exist between human to human as duplex.
- (ii)False Communication (0, 0, 1, 1): You are aware that the communications exists among nonhuman. The collected data representation nonhuman or machine to machine communications. It may contains communications among the animal to animal, animal to machine, machine to machine, or nonhuman to nonhuman etc.
- (iii)Uncertain Communications (0, 1, 0, 0): You are uncertain that the communications among human to machine or vice versa. It is like half duplex.
- (iv)Turiyam comment (t, i, f, l): The communication with self. It is the communication that does not require any human, machine, or animal. It is Turiyam awareness. The precise analysis of Turiyam awareness and its analysis can be helpful for self-motivation, healing several diseases and controlling depression.
- (viii)Turiyam Driving [23]: The driving is again based on Turiyam awareness rather than Red, light, or Green lights. It will become a more essential part when the automatic or self-driving car will be launched. It will require Turiyam mathematics to characterize the data sets in fourth dimension as follows:
- (i)True Driving (1, 0, 0, 1): The police aware that the given car was driving in true regions based on green lights.
- (ii)False Driving (0, 0, 1, 1): The police aware that the car is driving in wrong regions even though red lights were on. Same time the car is driving in the wrong zone rather than the left side.
- (iii)Uncertain Driving (0, 1, 0, 1): Police uncertain about car driving due to dynamic changes in direction.
- (iv)Turiyam Driving (t, i, f, l): The driving which knows that the goal of driving to reach safely. It is totally beyond the true, false, or uncertain regions. This type of driving focused on controlling the accident based on true, false, or uncertain driving regions. It is called Turiyam driving. It is indeed a requirement for self-driving or intelligent car.
- (ix)Social Network Analysis: The social network analysis for crime pattern or other decision-making analysis requires Turiyam mathematics as as follows:
- (v)True Relationship (1, 0, 0, 1): You aware that both person are friends and connected with each other at face book or social network also.
- (vi)False Relationship (0, 0, 1, 1): You aware that they are not real as well as social network friend.
- (vii)Uncertain Relationship (0, 1, 0, 0): They are partial friend at social network rather than real. They used to connect some time and disconnect or block each other some time.
- (viii)Turiyam Relationship (t, i, f, l): These type of friendship used to be hidden friendship. In this case, they never show their relationship at social network. These type of people connected as consciousness rather than connection, disconnection, or partial connection at social network. Even they get disconnected or never meet after some time. Still they respect or continue their relationship in a hidden way. These types of relationship can be called as Turiyam relationship. These types of incomplete relationship provide a new way to deal with incomplete context. It needs Turiyam awareness to explore the data and its pattern.
- (x)Incomplete Context: Let us suppose an incomplete attendance context shown in Table I. The student x1 attendance data is incomplete or undefined that the student came to the class y2 not. It needs proper approximation. These types of data can be approximated using the proposed method. There are three classes hence maximum 8 subsets exist as {∅,{y1}, {y2}, {y3}, {y1y2},{y1y3}, {y2y3}, {y1y2y3}}.
- (i)True graph: The information of student {x1} came to attend the subject {y1} and {y3} is true. It means that the graph containing subsets of {y1}, {y3}, and {y1, y3} can be characterized as true region and can be visualized via graph.
- (ii)Mislead Graph: The subset does not have {y1},{y3}, and {y1, y3} and represented the information about the attendance of student {x1}. It means the graph is represented using the vertex {y2}. It is misleading the information without scaling without proof.
- (iii)Uncertain graph : The graph that contains the subset {{y1y2},{y2y3}, {y1y2y3}} can be represented as partial or uncertain graph. It can be represented via membership values.
- (iv)Unknown or Nothing: There is no information about the student, he may bunk the class, he left the class, he dislike the faculty, and the faculty put absent due to his behavior.
TABLE I An incomplete attendance context
| y1 | y2 | y3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| x1 | 1 | ? | 0 |
| x2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| x3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
In the near future, the author will try to explore Turiyam mathematics and its application for multidecision process (Table II).
Table II The comparison of graph, mislead graph, uncertain graph, and Turiyam graph
| Graph | Mislead graph | Uncertain graph | Turiyam graph | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertex Known | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Edges Known | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Multi-Attribute | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Counting | Finite | Finite or infinite | Finite or infinite | Uncountable requires subset |
| Visualization | Static | Static and misinterpretation | Static and dynamic both | Dynamic |
| Application | Information extraction | Fake news, information pollution | Soft data | Dark data sets |
| Time | O(V×E) | O(V×E) | O(V×E) | Exponential |
| Issue | Visualization of large data | Misrepresentation and brings conflict among experts | Varies based on membership values of attributes | Exploration is one of the issues which is based on expert quantum cognition |
V.CONCLUSIONS
This paper proposed a method for characterization of unknown, undefined, and impossible objects in true (t), false (f), uncertain (i), and Turiyam (l) regions, independently using a defined subset. Same time the visualization of these types of data via graph (t), misleading graph (f), uncertain graph (i), and unknown or Turiyam graph (l) was also discussed with an example. In the near future, the author will focus on exploring Turiyam mathematics and its algebra for dealing with the data in four dimensions.