I.INTRODUCTION
Melanoma is a cancer that develops from pigment-producing melanocytes. Melanomas are most commonly found on the skin, but they can also develop in the mouth, pharynx, or eye. They are most common on women’s legs, while men’s backs are more common. They emerge from a mole with distracting changes such as skin disruption or collapse, constraint expansion, eccentric edges, and a dog change [1–3]. Exposure to strong light causes melanoma in people who have insufficient skin concentrations (UV). Ultraviolet (UV) rays can come from the sun or a variety of other sources, such as tanning beds. Moles make up around a quarter of the overall population. Risks certified in dynamics are those with different moles, a past full of influenced relationships, and a bad, safe distance. There are many amazing innate defects, such as xeroderma and growth risk. To confirm the diagnosis of any bothersome skin sore, a biopsy is performed. Utilizing sunscreen and maintaining a decent distance from UV light may kill melanoma. Treatment is ordinarily expulsion by the restorative method [4,5]. DNA damage caused by UV sunlight exposure is the most common cause of melanoma. Natural features can also be used to identify a community. The total threat of melanoma is clear with more than 50 moles. Tumors are less likely to damage the body’s diminished ability to resist disease cells in a weaker, safe environment. Following are the main reasons for cancer. Melanoma is caused by the bright radiation from tanning beds. Tanning beds are “malignant growth causing to humans,” according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer, and people who start using them before the age of 30 are 75% more likely to develop melanoma. People who add planes appear to have an all-encompassing threat, which is known to be an instantaneous result of progressively indisputable exposure to UV [6–10]. Exposure to brilliant radiation (UVA and UVB) is one of the main boosters of the melanoma movement, according to studies [11–15]. Melanoma is causally associated with irregular solar exposure (acknowledging “consume from the sun”). Melanoma is most usually detected on the back and legs of men and women (locales of sporadic sun introduction). It is more characteristic of fit and complete experts than unpleasant workers and is strongly influenced by budgetary concerns than internal and external jobs. The quality of the tumor silencer may fluctuate or disappear because of a range of circumstances. The use of sunbeds (which penetrate all UVA shafts), including melanoma, has been associated with the development of skin cancer. The strength and duration of sun exposure, the age of sun exposure, and hence the level of skin pigmentation are all significant factors in assessing hazards. Melanoma rates are frequently noted in countries where transients from northern Europe get a huge amount of brief, true sunshine that the skin of the pioneers does not change, Australia in particular [16–20]. Childhood introduction can be a more important risk factor than adulthood introduction. This is regularly identified in Australia during investigations. The fact that numerous certified sun absorbers exist increases the likelihood that the future sun will cause structural damage. Sunlight and tanning beds release UV radiation which increases the risk of melanoma and increases UV exposure in the vicinity of the equator [21–24]. A depiction of the ABCD (Asymmetry, Border, Color, and Dimension) run is as follows: start on the left side and work your way to the right: melanomas with (A) asymmetry, (B) an uneven, fatigued, or depressed edge, (C) concealment of different hues of darker, dull, or tan, and (D) an altered gauge width. On the plus side, ordinary moles do not have any unusual characteristics (no asymmetry, significant outskirt, even shading, and no adjustment in distance across). Melanoma in an H&E-colored skin sample – this case could indicate shallow-spreading melanoma. Metastatic melanoma has completely replaced the lymphatic center. Melanin is the main component of this drab color. Some advertisers use the term “progress” instead of “development.” Changing and producing moles will undoubtedly be concerning. However, other experts believe that the market is expanding. Although the height can aid in the detection of melanoma, the absence of an increase eliminates the possibility of melanoma [25–29]. The majority of melanomas are discovered before they become visible in the United States. When the increase is obvious, they may have gone to a more harmful level of interference. The framework has been represented to engage early area and give a wise methodology (with any advanced camera), yet its practicality has been tended to due to its weakness to adjust according to the changes [30–34]. Epiluminescence is a dermatologist term, and the analysis image is a dermatological image. It is an imaging framework used to take a gander utilizing a dermatologist on skin lesions. As illustrated, the analysis of skin cancer comprises multiple steps [35–39]. Figure 1 represents the process involved in detecting skin cancer. The input image is segmented using different image segmentation techniques, and proposed model is applied to the segmented image to classify the skin cancer.
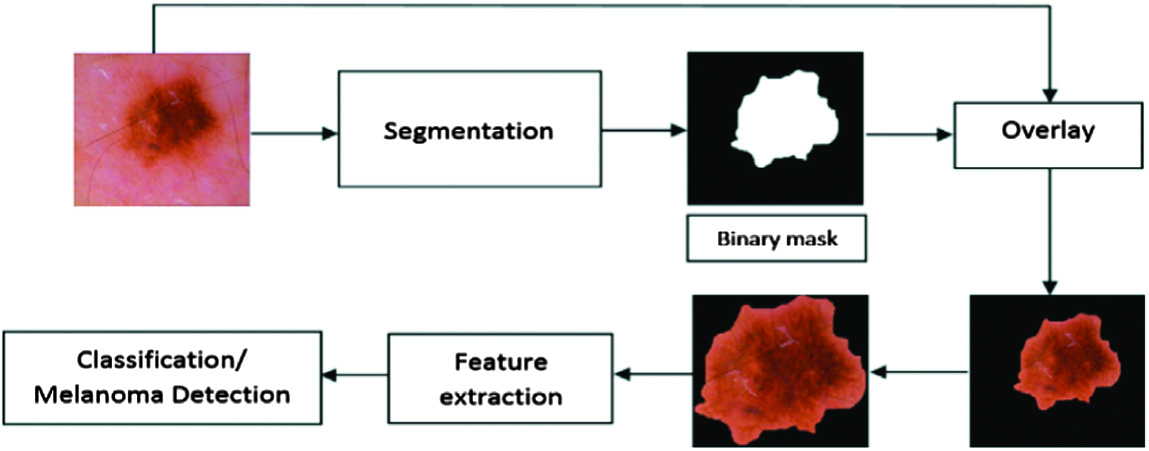 Fig. 1. Procedure involved in the detection of skin cancer.
Fig. 1. Procedure involved in the detection of skin cancer.
Image reclamation can be arranged in two ways: rebuilding from disturbance and rebuilding from cloud. Figure 2 addresses the preprocessing of the input image. In this case, the removal of hair is accomplished by morphological techniques, such as the disclosure of curvilinear structures.
 Fig. 2. Image preprocessing: (a) original image and (b) hair removal.
Fig. 2. Image preprocessing: (a) original image and (b) hair removal.
Figure 3 illustrates the different techniques used in image preprocessing. The process includes image enhancement, image restoration, and hair removal. The input image is enhanced by image scaling, color space transformation, and contrast enhancement. Image restoration is done to reduce the noise and prevent it from getting blurry. Different morphological and curvilinear methods are used for hair removal.
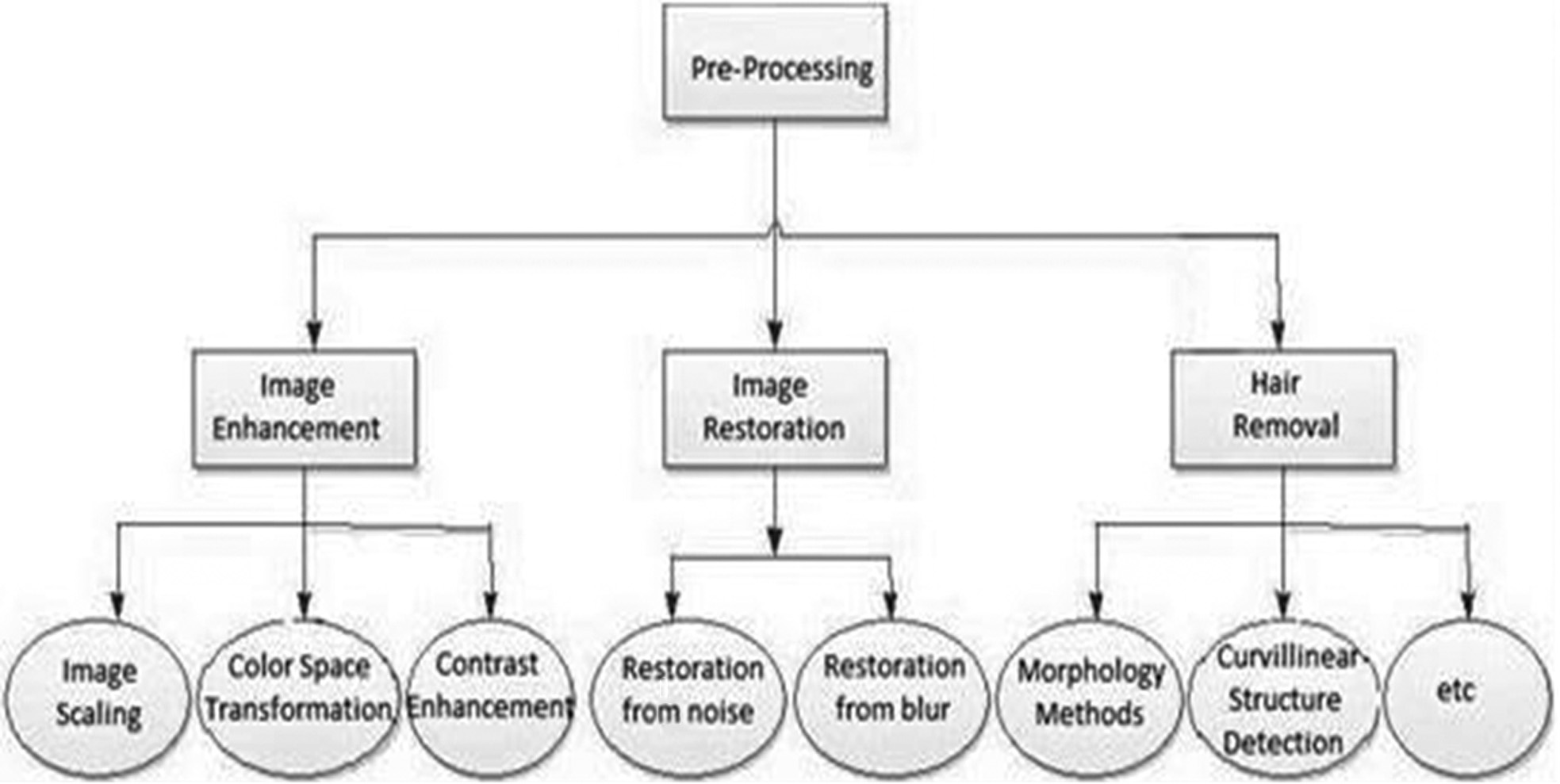 Fig. 3. Techniques of image preprocessing.
Fig. 3. Techniques of image preprocessing.
Figure 4 depicts the original and segmented image for the detection of skin cancer. In digital image processing and PC vision, image segmentation is the way toward parceling a digital image into different segments (sets of pixels, otherwise called image objects). Image segmentation is ordinarily used to find items and limits (lines, bends, and so on) in images [40–42].
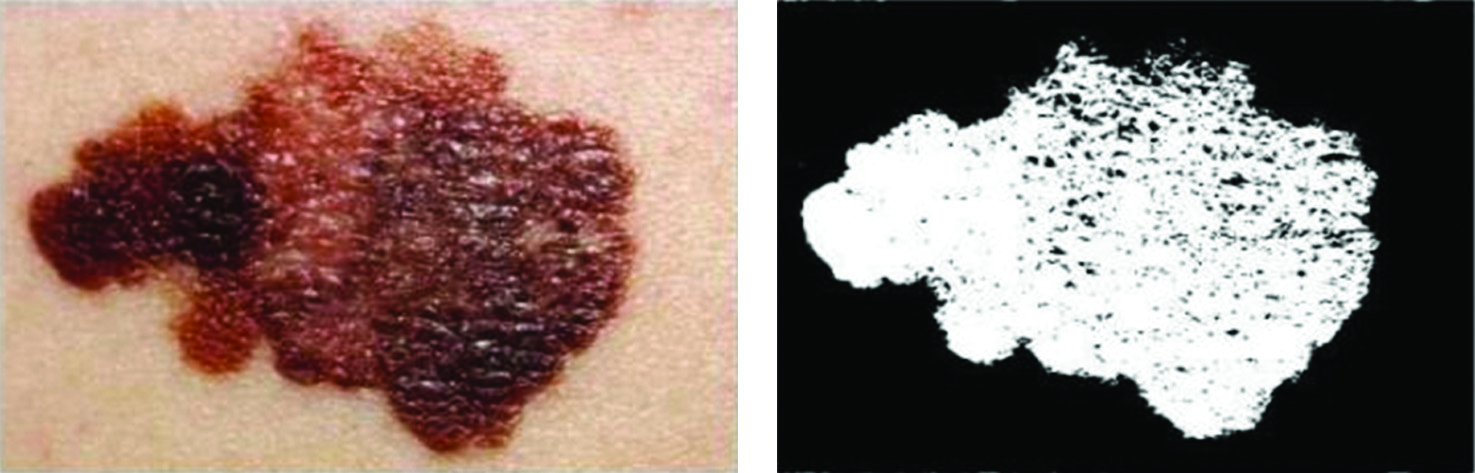 Fig. 4. Image segmentation: (a) original image and (b) segmented image.
Fig. 4. Image segmentation: (a) original image and (b) segmented image.
The analysis of the characteristics that appear in the case of a suspect is called the extraction of the characteristics. These are skin traits that occur when the risk of skin cancer is high [43–45]. Visual inspection is the most widely accepted symptomatic approach. Capricious moles still alive and well are normally regarded as contenders, break down moles as often as possible for alterations (form, size, shade, shake, or kicking of the bucket), and notify a certified specialist when a contestant occurs [15,16]. The memory associated “ABCD” is an important tool for the evaluation of melanoma signs and indications. A is for skin damage that is asymmetrical, B is for the border of the sore that is sporadic, C is for melanomas that have various hues when in doubt, and D stands for a dimension where moles more noticeable than 6 mm will most likely be melanomas than more diminutive moles. However, different melanomas are present as injuries of less than 6 mm in height, and when they first appear as a small spot, all melanomas are malignant. All the moles, including those with a diameter of less than 6 mm, are usually examined by specialists. False alarms can be caused by seborrheic keratosis when it satisfies some or all of the ABCD criteria. Specialists can distinguish between seborrheic keratosis and melanoma by examination or dermatology [17,18]. However, there is a variation in this model with an addition of E, which means endurance rates (ABCDE). When diagnosing and classifying melanomas, medical professionals look for these particular aspects of skin damage.
The implications found in the current study led us to work in this direction. Malignant melanoma is a typical cancer condition that is increasing these days with the increase in pollution, increase in exposure to UV rays, and other reasons. The classification of skin cancer in its early stages is of utmost importance. The work focuses on improving the accuracy of the entire classification process.
The main contributions of the current study are as follows:
- 1)We propose a model that aims to detect skin cancer at early stages.
- 2)We describe the method that includes machine learning (ML) and artificial neural network (ANN) techniques. It also uses the ABCDE rule with the ANN approach to process the data.
- 3)We experiment and then compare the results using performance metrics like specificity, sensitivity, precision, and accuracy.
- 4)The experimental results prove that the proposed model outperforms the current state-of-the-art techniques.
The paper is organized as follows: Section II discusses the related literature survey; Section III illustrates the proposed model; Section IV analyzes the results obtained; and Section V discusses the conclusion and scope for future work.
II.LITERATURE SURVEY
Most insurance and mammograms in this study are used to find out if the cancer is benign or malignant. The preprocessing of universal images was done immediately at the MIAS (Mammogram Image Analysis Society). Mass detachment was carried out with suitable edge esteem. At this stage, morphological screening was done for better segmentation. There was no distinction at the classification stage between large and malicious in the territory secured by the tumor and the surrounding region based on discrepancies of criteria. At the time of the research, the growing sporadic state of malignant tumor and their zones estimated the specified cutoff points. Sectional zones based on these qualities are called nanny and malignant [1]. According to the third assessment report on the goal behind the dangerous tumor passing, a spatial authentic examination was done on normal tainting factors causing harmful tumor in China. The study employed geographic estimates and Kriging additional contraptions, as well as spatial assortment models, to disperse the threatening rates of tumor destruction and thus the connected environmental sullying methods. The results show that the rates of destruction of hazardous tumors are spreading from east to west and establishing bundles of trademarks in specific regions. It is appropriate to observe the dispersion of the disease and its natural pollution factors using the real spatial distribution map. The map is also useful for geographically elucidating the unmistakable quality example of the disease, considering disease pathogenesis, and elucidating disease pathogenesis and sickness pathogenesis [2]. Malignant melanoma is far the most dangerous type of skin cancer. PC helped to diagnose melanoma at an early date by helping to establish frameworks for the classification of dermoscopic images. The segmentation of the skin-painful area is crucial for the exact classification of the image. In this investigation, scientific morphology was applied to segment the painful area for acceptable proof. Several shapes, surfaces, and shade highlights were extracted from a variety of dermoscopic images, and malignant melanomas were classified with an 85.71% of support vector machine (SVM) classification [3]. The protein and protein interactions (PPIs) should play an important role in changing parts of the fundamental and pragmatic relationships of the cell. Data about the nuclear parts of natural approaches are given. On the other side, PPIs connected to hazardous human neoplasms can provide insight into the science behind these neoplasms. In any case, a PPI database was not open until now. Makers have established HMNPPID, a database of protein–protein collaborations on human dangerous neoplasms containing PPIs of 171 various kinds of threatening human neoplasms. HMNPPID delivers explicitly harmful neoplasms to human administrations without investigating the proportion of biomedical labor, enhancing the capacity of research on PPIs in general for hazardous neoplasms. VisualPPI is also a discerning software that is used to speed up the screening of a certain PPI type for a hazardous cancer [4].
The purpose is to look at the distinctions between benign and malignant bosom illnesses in heated surface mapping (TTM). Hundred patients have been separated into three groups following TTM: typical patient, pleasant change, and malignant harm. TTM revealed that the malignant sore had warm highlights and a deeper layer with vessels around or into the vessel, an unpredictable warm example with a spinal cord in its bosom, a deeper layer of unusual warm source in the axilla, and an anomalous warm example with a round, space rock, and agaric form close to the one end of Angle of Louise of Br. The contrast between generous and malignant disorders is so clear [5]. Polarizability tissue imaginations are a form of structure that uses enticed light in order to investigate the tissue’s morphological and physiological features. Polarizability ellipsometric frameworks are often employed to depict dangerous thyroid tissue and obtain a handle on the combination of the sunlight polarization features. The established optical grid helps specialists to appreciate and examine the dangerous thyroid tissue quality as well as to check how the harmful thyroid tissue performs. The Mueller matrix for harmful thyroid tissue is exhibited, and photographs and features for depolarization, diatomization, and backwardness are collected from the pathology office of Gandhi Medical College, Secunderabad, India, employing threats to thyroid tissue instantly. Conditions will be addressed, and the polarization game plan will be applied during the novel, in pixel format, to the dangerous thyroid tissue during the novel and to techniques for organized Mueller matrix during the novel pixel-by-pixel evaluation structure and techniques for organized Mueller matrix of the dangerous thyroid tissue duration [6]. Skin disease is one of the most often recognized types of malignant growth. Its main disclosure enhances results and extends human lives. Melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and epithelial cell carcinoma are three well-understood types of skin cancer. Melanoma is a melancholic cancer and non-melancholic cancer for basal cells and epithelial cell carcinoma. Regardless of the identification of these malignant growth types using a skin biopsy, personal recognition of skin disease using modernized methods might lead to a speedier and exact diagnosis. The bulk of the techniques of professional motorized skin disease have so far concentrated unequivocally on the dangerous melanoma type. In the absence of adequate datasets with different types of harm, no complete investigation could be carried out on non-melancholic hazardous skin injuries. Customized evidence of hazardous pigmented skin damage is being investigated currently. Two advanced skin sore distinctive procedures of dermatologists are required for this. The skin aches are initially characterized using a major learning model as melancholic or nonmetallic, and hazardous types are subsequently recognized with other significant learning models. Melancholic and non-melancholic skin wounds, according to display assessments, are associated with the most essential accuracy. It also reveals that melancholic-threatening skin injuries are usually more accurate than threatening non-melancholic skin injuries [7]. The authors in [8] examined the stage appropriation of typical and malignant lymphoma cells by utilizing advanced holography. The tentatively gotten stage image uncovered an unmistakable surface that can possibly be applied to malignant lymphoma distinguishing proof. Microwave frameworks, such as cancer treatment or imaging research or spectroscopy, for biological applications are seemingly promising. Their use is dependent on knowledge of the dielectric characteristics of tissue, especially a clear distinction between threats and usual tissue. Since most studies have concentrated on the dielectric features of ex vivo tissues, it is necessary to understand human tissues more biophysically. The paper looks at the dielectric properties of unadulterated glucose, glucose in action courses like appearances of natural tissues that plan to think at its sign in carcinoma cells, and glucose in action pathways such as appearances of natural tissues that plan to think at its sign in carcinoma cells using microwave strategies. Clear and understandable theoretical plans are employed for the unequivocal demonstration of difficult permittivity. The preliminary results of these assessments and their review are presented [9]. The most potent type of skin cancer is melanoma, and one of the most common malignancies is malignant melanoma. It can be treated if malignant melanoma is found early on. The two main causes of melanoma are overexposure to sunlight and hereditary factors. A total of 132,000 people worldwide are affected by skin cancer every year. Early choice will not only save people’s lives but also the natural world’s beauty. Processes of imaging are crucial for the detection of malignant melanoma. In this research, a judgment is made based on the relationship factor established from the pixel power grid of ordinary and odd mole images. The results acquired for a large number of photos show that the technique provided is able to detect malignant melanoma [10]. Divalent cations have a number of biological functions, including oral discouragement. The aim was to see whether the presence of potential divalent cation unions in serum-distinguished patients with oro-maxillofacial tumors in a control group without dangerous malignant growth pathology (Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe2+, Zn2+, and Cu2+) (at some other level). The Maxillofacial Surgery Clinical Hospital “Sf. Spiridon,” Iasi, evaluated 104 adult patients with basic phase II and III hazards, limited to lips, tongue, oral mucosa, and salivary organs for 2 years, and divided them into two categories: differentiated and controlled. Spectrophotometry for atomic ingestion was used to collect serum from the studied cations. The focus of our research was the critical decrease in the obsession of zinc and copper in serum and increases, both in serum and spit. There is a reduction in the amount of serum zinc and copper centers. In relation to the serum iron value (mean standard deviation in mg/L), for women and men in the control group and broadly, the social affair of patients with endangering malignant growth in the oral and maxillofacial regions has been different from the qualifications of quantifiable vitality [11]. Early diagnosis of malignant tumors is a critical first step in the discovery of mammographic cancer zones. Although many discovery plans have been developed, they are still unable to eliminate all threats completely. The creators propose using fractal inspections and space minutes as tools for preparing pictures to classify obscure test mammograms. In conjunction with these methods, a backpropagation neural system and a self-sorting guide are used. The histogram of the space minutes at low demand shows that discerning images of space minutes cannot be distinguished between generous and malignant mammograms. Both the two-arrange backpropagation neural system and the one-arrange self-sorting guide provide 70% accuracy and low false-positive rates. The presentation of these classifiers could also be improved with further preprocessing and progress [12]. Microwave ablation (MWA) is a less-invasive therapy approach for malignant tumors. This research discusses a thin interstitial implement that provides an almost circular clearance zone in malignant liver tumors and investigates how the nature of the MWA technique is affected by activity recurrence. The study next suggests a comparable but much shorter MWA method [13]. Quantum cascade laser infrared (QCL-IR) microscopy has the potential to become a one-of-a-kind approach for histology segment diagnosis. The goal of this pilot study is to see if benevolent and malignant bosom histological segments can be distinguished using synthetic profiles and without the use of geographical data. The test consists of 22 independent samples chosen at random from paraffin-installed stumbling blocks with an equal number of kindhearted and malignant marks.
Honda, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, Tanaka, and Tanaka are all very popular. Given the shading data from photos, this research tries to find highlights to help analyze the disease as malignant melanoma. The designers divided the RGB area into 4096 pieces and picked regions with malignant melanoma in particular colors. Only shade information might be used to delete about 26% of melanoma pictures by taking advantage of these gaps. This is critical for the precise identification of malignant melanoma [14]. A micromachined millimeter wave test was employed to confirm a mouse skin malignant growth model that was enhanced for the initial period of acanthoma assurance. Since the difference in S11 between risky melanoma acanthoma and sound tissue incorporation is 6.7 events greater than normal standard estimates deviations at a comparative site, the threatening melanoma tumors clearly distinguish from the strong tissue involved. In addition, the test has 8-fold greater selectiveness for a tumor growing within the skin on the edge of the surface compared to a subcutaneous tumor secured underneath a thick, stable membrane. This shows the enhanced application of the test to the top section of the skin, where the advancement of acanthoma in severe melanoma patients begins [15]. Reference [16] demonstrates a surface segmentation technique for malignant pleural mesothelioma using thoracic CT outcomes. The designers employed a combination of automated and human inspections in the surface investigation stage to separate factual highlights from the MPM surface. This technique repeats the entire CT volume for the segmentation organization and chooses pixels that satisfy the quantitative criteria removed. The technique provided demonstrated a reasonable closeness rate (J = 0,73) between the soil truth and the volume of MPM produced during the test [17]. PC-assisted frameworks in a variety of therapeutic applications are presently vital. This study supplied yet another computer-assisted diagnostic (CAD) framework for the classification of pneumonic bugs as malignant and considerate. The classifiers of the bagging-choice trees were used. Appraisal for classification is established by the 86.8% precision of classifier with an affectability of 94.7% and reliability of 0.950AUROC; affectability of 80.0% and insult class of 0.888AUROC; and affectability of 77.8% and questionable class of 0.935AUROC [18]. Computer-assisted identification frameworks can be used by radiologists to allow them to find pneumonia early. In this study, a unique computer that helped the diagnostic framework is proposed to classify aspiratory buttons as malignant and considerate (CAD). The suggested CAD system achieves good classification performance with troop learning classifications, which provides radiologists with significant support throughout the disease conclusion procedure [19].
Medical imaging is vital as a range of techniques are currently being used, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Computed Tomography scan (CT), laparoscopic and endoscopic operations, and cancer analysis. Creators explore many ways for segmenting photographs that have uncertain local boundaries. Traditional segmentation approaches work poorly on noble images, such as histological images. This paper describes a few ways for segmenting images like tissue pictures. The authors examine classic histology segmentation algorithms and compare them to an ongoing system with a good histology dataset. The creators portray the processes used to diagnose cancer and tumors in the quest for malignant tissues [20]. A randomized, cross-controlled basis for investigating the effects of stomach needle therapy on the treatment of threatening patients with near-home satisfaction (QOL) in Shenque qi scattering chemotherapy was obtained. A total of 26 cases were allocated randomly for treatment under group A and group B, according to their quantity for chemotherapy (as measured by the EORTC QLQ-C30 V3.0 and Karnofsky score); chemotherapy was split into two periods (the first chemotherapy period and therefore the ensuing one). In group A, patients recognized the arrangement for therapeutic measures during initial chemotherapy and then received controlled action during the subsequent chemotherapy; likewise, patients in Group B recognized the sport plan for controlled measurements during the initial chemotherapy and received accommodation measures during the following chemotherapy. Due to the independent assembly of the treatment and control bundles, medical and controlled measurement data have been analyzed [21]. The administrators of the most lethal, threatening skin disease melanoma are ready to mass screen skin bruises of people at great risk for early revealing and thus optical imaging of skin injuries. Surface lighting-based technology, such as epiluminescence light microscopy (ELM) epiluminescence via ldquoDermascopyrdquo, has shown a lot of potential to detect deadly melanomas at an early stage. In the separation of pictures for key vascular information and subordinate information, the limits of image structures based on surface reflectance are recognized. The Nevoscope has been produced by manufacturers as a one-of-a-kind optic imaging system using multispectral transillumination to image wounds in the skin, showing subsurface coloration, as does information on blood volume based on vascular construction. This work will explore the possibility of transillumination of multispectral Nevoscopes to distinguish and dismantle ratiometric estimates using epiluminescence imagery to separate malignant melanomas from dysplastic nevi or other conventional skin lesions [22]. The authors in [23] describe a Tactile Cyber-Physical Imaging System (TIS) for the detection of malignant tumors. In the detection, the rule of all light within reflection terminal innervation ratio (TIR) is applied. CP-TIS assesses the mechanical characteristics of the installed objects such as size and flexibility (e.g., tumor). A damage score based on the mechanical properties controlled by TIS can be generated, because studies reveal that malignant tumors are often larger and more rigid. One subjective way for specialists to diagnose early breast cancer is the Clinical Breast Examination (CBE). However, this strategy is useful only for recognizing damage and not for preventing injury to the tumor. In addition, this is an emotional method in which the presentation is based on how the experts conduct CBE. In this strategy, measuring the mechanical properties of a tumor to discriminate between target tumors is useful. The objective of cutting off an ultrasonic image is to smooth out homogeneous regions and protect the edges and basic data to highlight the demonstrative characteristics of the image. A complete dataset of 64 images of B-mode liver ultrasound, including 19 hepatocellular cell carcinomas and 45 metastatic carcinomas, uses several methodologies, such as neighborhood-based strategies, middle-sifting, geometrical separation, and anisotropic dispersion. The differential analysis between hepatocellular carcinoma and the metastatic carcinoma atypical cases is regarded as a discreet assignment, as the acoustic appearance of hepatocellular carcinoma and the atypical metastatic carcinoma is profoundly covered. Furthermore, in the present work, the abstract examination is more likely to bury and fluctuate in the spectator, resulting in a) smoothing homogeneous territories by processing the metric peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR), (b) preservation of the edges (by registering the Focus on Microsocopy (FoM) list), and (c) structuring/highlighting the protection of the spectators (by figuring out SSIM list). The comprehensive analysis targets the image processed by the Lee Sigma technique based on local statistics to the highest effect in terms of smoothing, edge, and structure/highlight protection [24].
Cognitive informatics is drawn from both the cognitive and information sciences. Its primary focus is on human information processing, mechanisms, and processes within the context of computing and computer applications. Cognitive informatics is an interdisciplinary field. The classification of skin cancer, which is receiving a lot of attention in the field of health informatics, is the primary emphasis of this work. The goal of cognitive computing is to address complicated issues by developing computer systems that can behave and reason like humans. The ability of humans to solve difficult problems is augmented by AI. The provision of accurate outcomes is the primary objective of this system. It does this by imitating the way humans think in order to discover answers to difficult questions. The primary focus of the manuscript is on the application of computer modeling by means of ANNs to explain human intellectual capacities for the purpose of early identification of melanoma. By taking the human mind as an illustration, a cognitive healthcare system, like the human mind, forms opinions based on its capacity to acquire and understand information. As a direct consequence of this, conventional forms of medical data, such as laboratory results and clinical notes, are now capable of being compiled and analyzed. The utilization of health informatics in the model that was proposed was helpful in accessing, analyzing, and understanding the existing health data and information, which paves the way for the planning, improvement, and delivery of patient services and care.
III.PROPOSED WORK
A 400× lens system and a 400× optical focus were used to produce histological pictures of the skin tissue. During Mohs restore-style methodology, the tests have been colored with hematoxylin and eosin, a thorough procedure including the removal of little skin layers with malignant development and the separation inside the amplifying focus, thereby eradicating the tumor constantly till solid tissue remains.
A total of 100 events (49 sound models and 51 serious melanoma tests) have been collected by the Pathology Unit – Hospital First Statel Mar – Parc de Salut Mar as dataset (Barcelona, Spain). The initial step is the preprocessing of images.
Stage 1: Image Preprocessing: Histological photos were modified to eliminate the margins and transform the images to a dim scale. The cell centers, for example, were exhausted using a clear threshold (I120 = 1) or cytoplasm (I120 = 0) according to its capacity (I). In order to isolate centers from other inconsistent low-power areas, every related image with less than 30 pixels was eliminated. Finally, a double expansion was required by a paired deterioration to enhance the altered division and fill the openings into the divided while keeping the centers alive and unmodified.
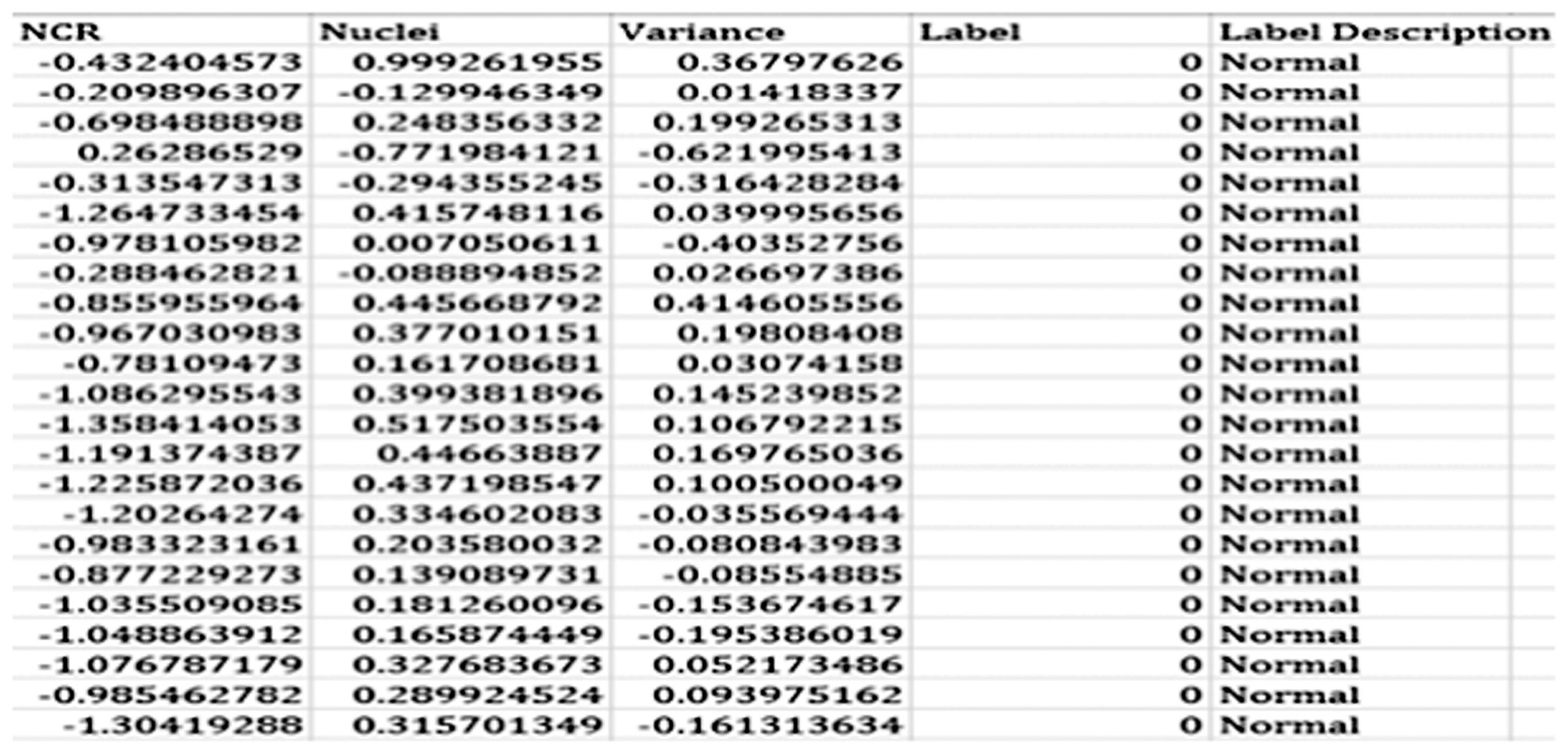
Stage 2: Feature Extraction: Harm is portrayed by the abnormal and uncontrolled advancement of cells and the way these assault bordering tissues. The properties of cancer-causing tissues are seen by pathologists through microscopic anatomy examination and used for assurance functions. During this assessment, three essential tissue options were removed for the ensuing portrayal task: nuclear cytoplasmic extent, centers variety, and pleomorphism (measure contrast). Figure 5 represents the dataset in Excel format.
Stage 3: Artificial Neural Network Classifier: Acquiring information – training and testing set. The data are imported into Mathematica from the.xlsx files and dispersed among data sources and targets. Seventy models will be randomly selected from the 100 available models to develop the ANN replacement.
A.PROPOSED ALGORITHM
Step 1: The total algorithm for analysis works in two faces: training and testing
Step 2: The implementation is presented with two operations: 1. Train Model and 2. Perform Testing.
Step 3: In the training phase, ABCDE rule with the ANN approach is processed, where A conspicuous methodology for reviewing the signs and indications of melanoma is the memory-associated “ABCDE”: asymmetrical skin sore; border of the sore is sporadic; color: melanomas when in doubt have various hues; diameter: moles more noticeable than 6 mm will most likely be melanomas than more diminutive moles; enlarging: enlarging or creating.
Step 4: The second phase is the testing phase, and the first user input is the testing image.
Step 5: The features are extracted using the ABCDE approach.
Step 6: The classification is performed on the basis of the testing model created in the training phase.
Step 7: Classification of sample is done.
B.IMPLEMENTATION OF PROPOSED WORK
The execution work is performed on Matlab R2011a. The augmentation of the bottom work territory work and therefore the proposed work is finished by masterminding the graphical user interface (GUI). The GUI, a part of the Matlab, essentially allows us to form the screens by pulling the controls on the workspace. The structures that we make within the Matlab are referred to as figures.
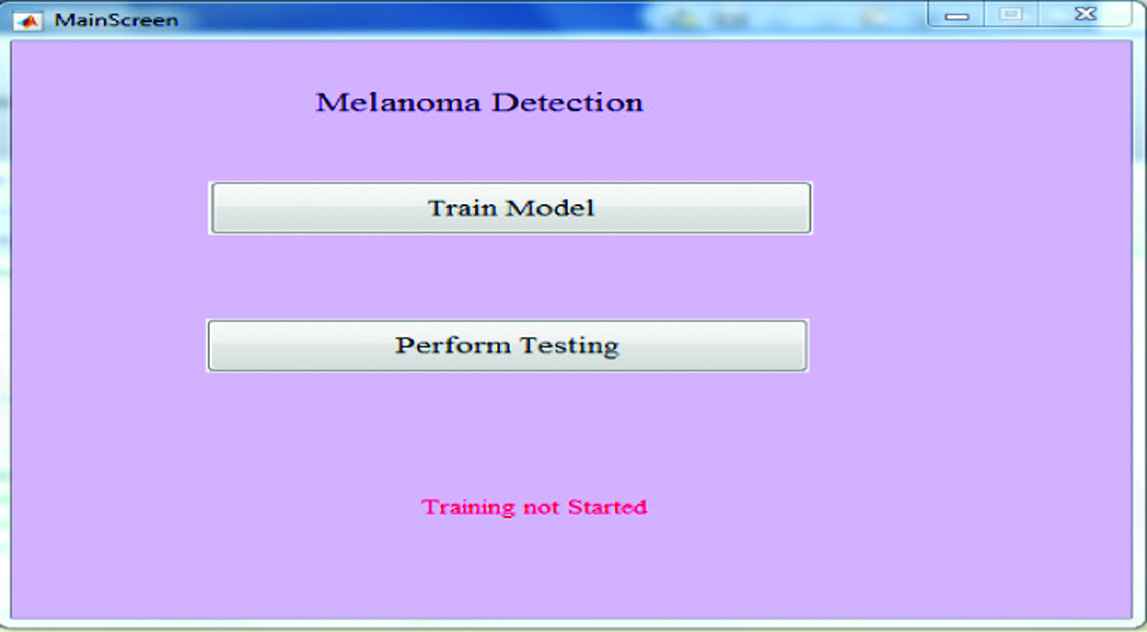
Fig. 6 shows the main entry screen for the implementation. On the main screen, we have two options: Train Model and Perform Testing. In the initial level, the label shows the training has not started as we have not clicked for the training of the model.
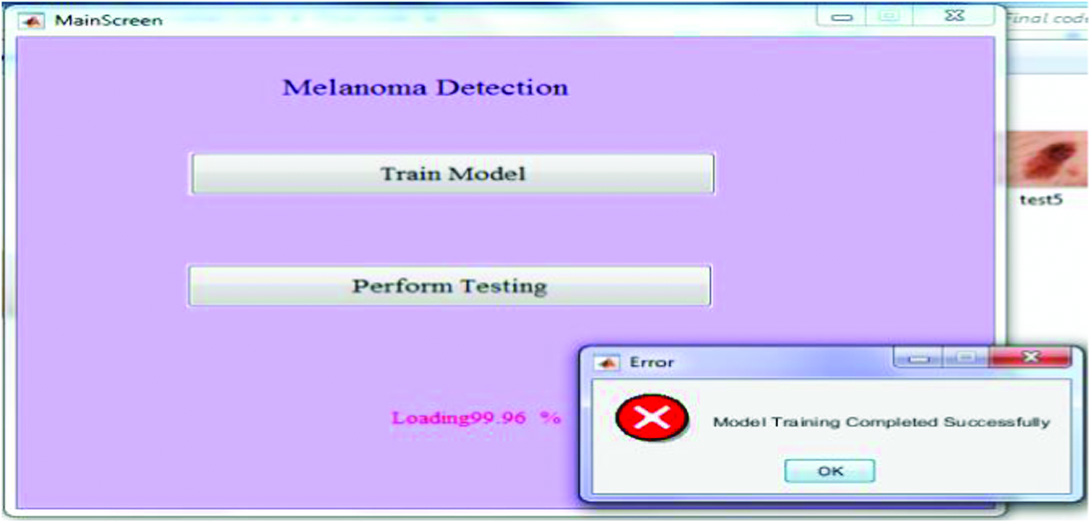
We have provided the training process for the model of melanoma recognition in this phase, and progress is shown on the mark in the percentage of model training. We have put the disease-related images in the database folder for the purpose of training the model. The melanoma detection, phase test form (Fig. 7) provides the options for selecting the test image to be used for analysis, detection, and image classification.
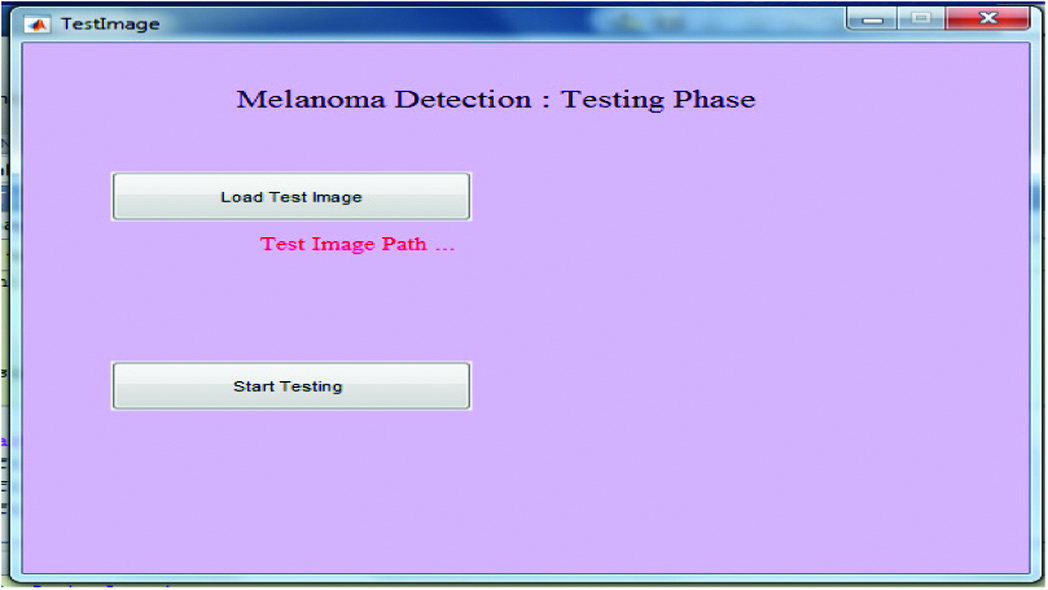
Fig. 8 shows the image selection dialog box, which will appear when we click over the button Load the test image; in this, we have to select the image that is used to perform the testing. The absolute path of the complete image is shown on the label, indicating the location where the image is present. When we click on the start analysis, then the analysis is done on the basis of the ANN approach and using feature selection, medial separating, and histogram prepossessing to maintain a strategic distance from the uneven illuminance issue. Then, a novel image segmentation algorithm (Otsu) is utilized for sore extraction. The extraction of ABCD is done by novel methodology, and the total dermoscopic value is used to characterize the weight coefficients. Figure 9 illustrates the classification of cancer.
IV.RESULT ANALYSIS
The testing set (testing set size = 30) has been utilized to review the starting late-orchestrated ANN. To accomplish everything considered, the introduction measures have been settled: affability, accuracy, demeanor, and precision.
A.TEST CASE 1
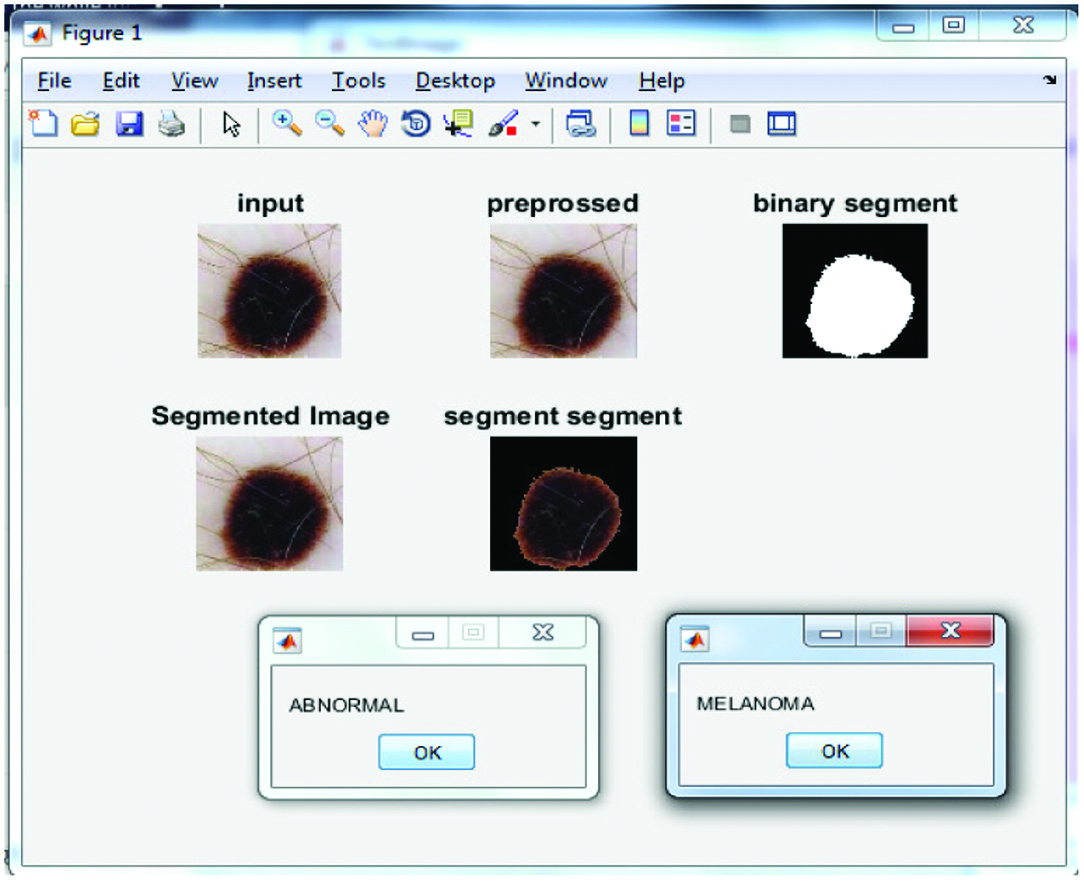
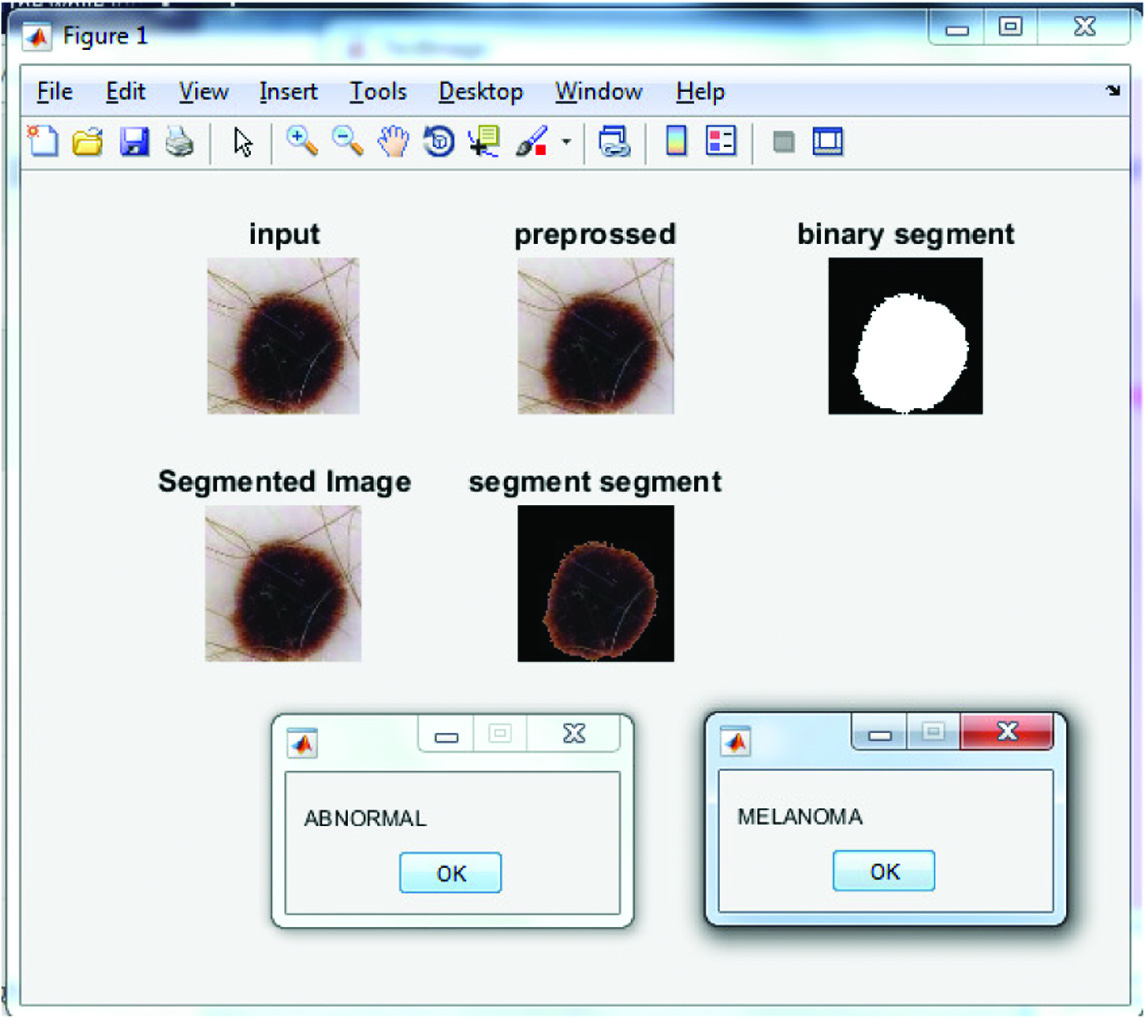
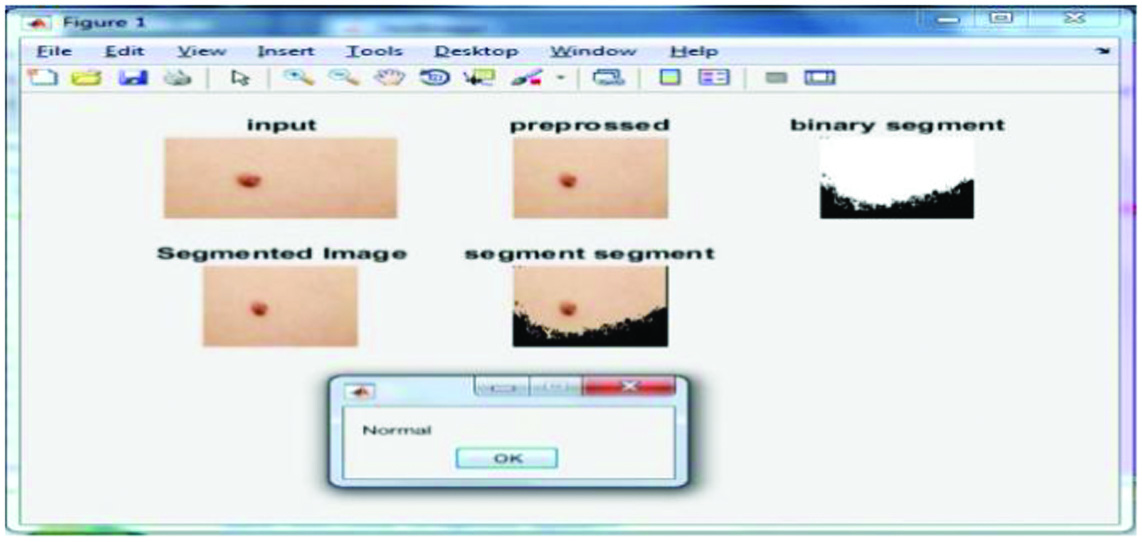
The result which is performed on the basis of the proposed approach is shown in Fig 10.
B.TEST CASE 2
Figure 11 represents the results obtained from the proposed algorithm on the execution of second test case.
III.TEST CASE 3
Figure 12 represents the results obtained after executing the third test case.
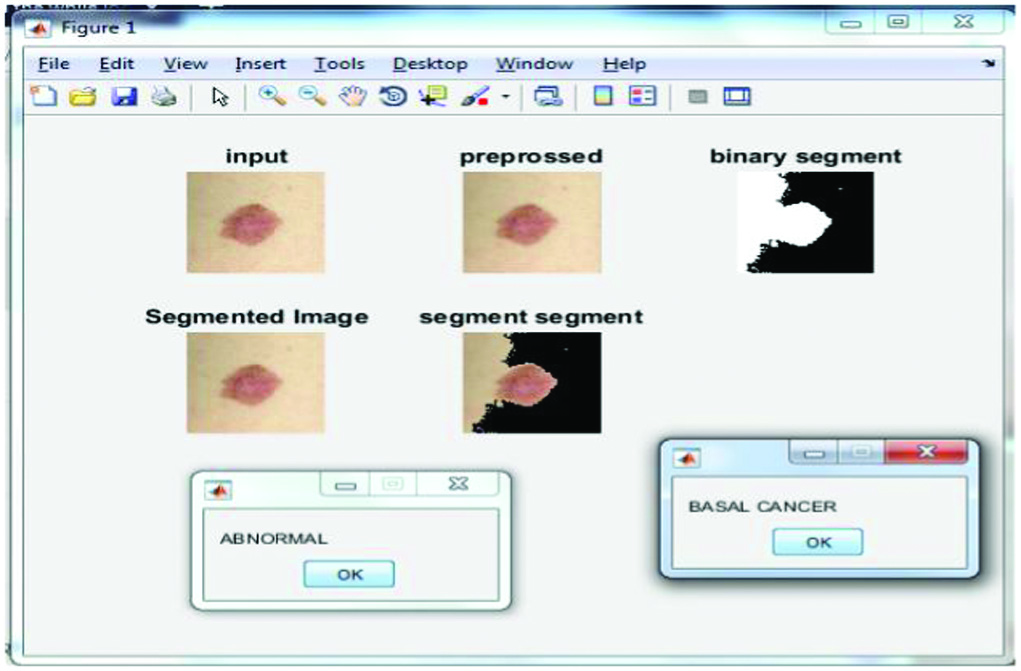 Fig.12. Result of Test Case III.
Fig.12. Result of Test Case III.
Overfitting should have been avoided as our classifier seemed so good. A real model describes an abstract error or change instead of a core relationship in overfitting. Overfitting happens if a model is too flexible, such as when the measurement of perceptions involves incalculable components. Because it overreacts to small changes in the arrangement data, such a model is poorly visualized. Overfitting happens when the model starts “holding” the planning data instead of “learning” to outline the model. Table I illustrates the results obtained from the proposed model.
Table I. Result analysis of proposed work
| Performance measure | Value |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 1 |
| Precision | 0.933 |
| Specificity | 0.933 |
| Accuracy | 0.933 |
Table II illustrates the sample images taken and their corresponding classifications of skin cancer.
Table II. Samples analysis table
| Image sample | Test result |
|---|---|
| MELANOMA | |
| MELANOMA | |
| MELANOMA | |
| NORMAL | |
| NORMAL | |
| MELANOMA | |
| SQUAMOUS CANCER |
In Table II, we have shown the testing of the samples which we have tested using the implementation and proposed methods, and the number of samples is also checked, which resulted in the proposed accuracy of 93.33%.
Figure 13 illustrates the performance analysis of the proposed method through the different performance metrics.
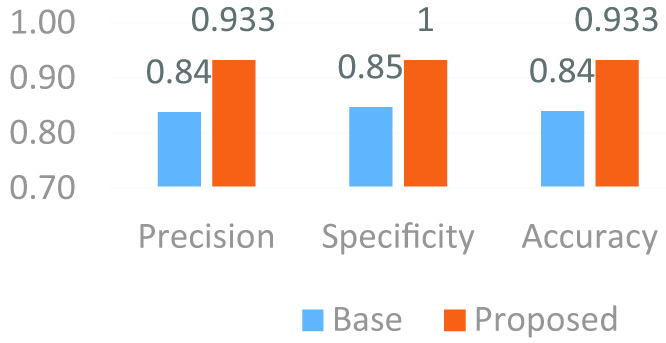 Fig 13. Performance analysis of proposed method.
Fig 13. Performance analysis of proposed method.
Table III analyzes the proposed model based on the metrics taken into consideration and finds that the proposed model has better results in terms of accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity compared with current state-of-the-art techniques.
Table III. Comparative analysis of proposed model with existing state-of-the-art techniques
| Ref no | Year | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [ | 2018 | – | 89.4 | 64.4 |
| [ | 2018 | 76.5 | 96.3 | 89.5 |
| [ | 2019 | 89.43 | 91.15 | 87.71 |
| Proposed model | 2023 |
V.CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
The most significant risk factor for melanoma skin cancer is unprotected exposure to UV radiation, a way to detect melanoma, the most dangerous kind of skin cancer. These are the suggested methods: locating and removing hair with adapted main curvature, segmenting skin lesions with color normalization, and locating melanoma with feature extraction from skin lesions using the ABCD rule. Finding the hairs is simplified by the principal curvature’s ability to adapt. Because color normalization eliminates the impact of shadows and illumination, even the tiniest skin blemishes may be seen. The terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (TDS) score is assessed with the use of the ABCD melanoma detection criteria. The proposed method has demonstrated promising results in a wide variety of applications, including hair identification, skin lesion segmentation, and melanoma detection. Due to the varied resolution of the photos in the ISIC collection, it is challenging to detect the sizes of skin lesions across shots. For this reason, it is important to examine data regarding the diameters of skin lesions. However, this problem can be fixed by either requiring all images to adhere to a regulation or standardizing their resolution. As a result, it is important to create technology that can identify melanomas quickly and accurately. However, the approach is machine-dependent, since images from a melanoma analysis are collected in a medical clinic as an epiluminant image by a form of explicit machine. This uses a high-resolution shading image of skin lesions captured using a high-resolution camera/gadget as well as an approach to picture preparation. The first step in this effort is to take high-resolution pictures of skin injuries rather than epiluminant pictures captured by devices in healthcare establishments. Machine training to characterize a classification limit will be followed by highlight extraction.
Future Work: Researchers may employ full-body pictures in the future to provide a clearer response to this topic. Autonomous, full-body photography has the potential to greatly increase efficiency and make photography more mechanical. An emerging idea in deep learning is auto-organization. Auto-organization is an unsupervised learning technique that examines data samples to reveal salient features and latent links or patterns in images. Convolutional neural networks can be used to enhance feature retrieval in expert systems. The testing of the auto-organizational paradigm is in its infancy. However, understanding it can aid in the development of more precise image processing systems; this is especially important in fields like medical imaging, where every detail is crucial to making an accurate diagnosis. In the future, these approaches will be implemented in the real-time environment and also will like to work on convolutional neural network (CNN), and other modern approaches will also like to work on the detection of the other types of cancers.