I.INTRODUCTION
The creative economy has become one of the key pillars of global economic growth and has increasingly helped GDP in many countries. This sector continues to extend into different fields, such as fashion and culinary arts, as well as music design, visual communication, film and animated videos, architecture, photography, and video games, each of which represents significant potential [1]. In Indonesia, the character-based intellectual property (IP) industry is a key element in the creative economy that encompasses animation, comics, video games, films, and products. Well-developed IP characters can not only serve as an entertainment product but also as strategic assets of different business models, from licensing and franchising to their integration into digital platforms.
Despite its potential, Indonesia’s IP ecosystem faces constant challenges, including limited creator access to global markets, a lack of transparency in IP monetization, and underdeveloped licensing and distribution networks, which hinder industrial scale [2]. Numerous local IP creations, such as Si Juki, Tahilalats, Emak Matic, and Battle of Surabaya (Fig. 1), have gained significant international recognition in various formats, such as comics, films, animated TV series, and products. These characters celebrate local identity and cultural knowledge, while at the same time having significant commercial appeal, especially when exploited through licensing, cross-industry collaboration, and SI-driven digitization.
 Fig. 1. The characters of Si Juki, Tahilalats, Emak Matic, and the Battle of Surabaya.
Fig. 1. The characters of Si Juki, Tahilalats, Emak Matic, and the Battle of Surabaya.
However, monetization and distribution of local IP remain limited, especially when competing with established global properties. Barriers include low investor accessibility, limited marketing platforms, and insufficient mechanisms for copyright protection [3]. AI-based IP valuation, digital copyright management, and the integration of stakeholder-specific panels into a single, scalable digital platform are still uncommon in the current ecosystem. Bhinneka.Space addresses these gaps by offering a smart digital hub designed to strengthen Indonesia’s IP ecosystem through technology-driven solutions.
With the rapid advancement of digital technology, artificial intelligence (AI) has become a critical driver in the creative industry, Anantrasirichai [4], including the development and distribution of character-based IP. AI makes it possible to optimize the creative process, streamline copyright management, and improve connectivity among stakeholders across the industry ecosystem. Leveraging machine learning, big data, and blockchain analytics, OCA can facilitate automated matching between creators, investors, and distributors, improving efficiency across the characters’ IP supply chain. In this context, the System II-based digital marketplace is critical to connecting differences in Indonesia’s IP ecosystem. This platform can be a bridge between creators, productive studios, investors, publishers, and consumers, promoting a more integrated, transparent, and sustainable ecosystem. Bhinneka.Space presents itself as a smart digital hub and disseminates systems based on the System II system to optimize the characters’ IP supply chain, drive business model innovation, and foster the growth of the Indonesian creative economy.
In recent years, the concept of markets promoted by KLEA has spread considerably within the creative industry, especially in digital arts, animation, and comics. Global platforms such as Tomic’s, Art Station, Open Sea, and Behance demonstrate that technology can facilitate the monetization of creations while also connecting creators with global audiences. For example, Toomics, a digital comics platform, applies AI algorithms to recommend content tailored to user preferences, while Art Station allows illustrators and 2D/3D creators to sell their work directly to international clients [5]. These models show the potential of II on creative industry platforms to improve user engagement and increase market reach.
At the same time, business models within the IP supply chain are evolving as platforms are increasingly able to improve the efficiency of distribution and licensing. IS technologies can analyze market trends, automate copyright management, and optimize creator-investor matching [6]. According to empirical evidence, access to the digital supply chain of AI can reduce transaction costs, improve market accessibility, and improve transparency in the monetization of IP.
Indonesia’s IP ecosystem has attracted creators, production studios, investors, publishers, and distribution platforms, each of which plays different roles in the IP development lifecycle. Studies have shown that industries with a well-coordinated supply chain and integrated stakeholder collaboration generate economic and sustainable value [7]. This underscores the importance of fostering easy communication across the creative industry and in strategic partnerships.
Bhinneka.Space responds to this need and offers a digital marketplace powered by Ria, specifically designed to connect fundamental inequalities in Indonesia’s IP sector [8]. Combining AI with cloud computing technologies aims to improve cooperation processes, expand creators’ access to global markets, and establish more efficient data-driven business mechanisms to develop, distribute, and monetize characters’ IP [9]. The integrated ecosystem model directly addresses critical challenges such as fractional supply chains, limited inter-official networks, and low global visibility, ultimately positioning the Indonesian IP industry to improve international competitiveness.
A.STUDY PURPOSE AND SCOPE
The aim of this research is to provide an overview of the development process and the main functionalities of Bhinneka.Space, with a specific view of the features based on the II [10]. One of the core elements of the platform’s technology capabilities is automated IP valuation, data-driven licensing decision-making strategies and processes, and conjunctural stakeholder characteristics that collectively improve operational efficiency within the ecosystem.
The study also identifies the main players in Bhine’s space ecosystem and discusses how they enable insight into their relationships, unify resources, and develop innovative business models [11]. These interactions are critical to sustaining the growth of the Indonesian IP industry and promoting a competitive creative economy.
Ultimately, the aim of this research is to create actionable insights into the transformative potential of AI in the characters’ IP sector, highlighting its role in creating new business opportunities, facilitating creative synergies, and strengthening Indonesia’s position in the global creative economy [12]. By promoting the adoption of integrated digital ecosystems like Bhinneka.Space, differences between stakeholders can increase Indonesia’s sustainable economic growth and cultural assets on the world stage.
B.STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS AND FUTURE PROSPECTS
Looking ahead, the development trajectory of Bhinneka.Space is expected to prioritize several strategic directions:
1.Enhancement of AI intelligence
Strengthening AI capabilities to conduct more sophisticated market trend analyses will provide stakeholders with actionable, data-driven insights to navigate the rapidly evolving character IP landscape.
2.Optimization of User Experience
Continuous refinement of AI-driven functionalities will improve usability, adoption, and retention across all stakeholder categories: creators, investors, and consumers. Enhanced personalization features will further increase engagement and satisfaction.
3.Expansion of Monetization Mechanisms
Integrating diversified revenue streams and refining payment structures will promote an inclusive and equitable ecosystem that rewards creativity, innovation, and investment fairly.
4.Global Collaboration and Market Access
Partnerships with international distribution platforms and studios will open new market channels for Indonesian character IPs, enabling local creators to gain visibility and competitiveness in global markets.
5.Broader Impact and Alignment with SDGs
From a macroeconomic perspective, Bhinneka.Space aligns with United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 8 (decent work and economic growth) and SDG 9 (industry, innovation, and infrastructure). The platform supports:
- •Economic Growth: By stimulating IP-based industries and expanding market access.
- •Quality Job Creation: By enabling creators, developers, and related professionals to access new income streams.
- •Innovation Infrastructure Development: Through the establishment of AI-powered digital ecosystems tailored to the creative sector.
This strategic alignment not only analyzes the local needs of the Indonesian creative economy but also promotes the global goals of inclusive, knowledge-based, and innovation-driven economic growth [13]. With its integrated model, Bhinneka.Space serves as a catalyst for integration into a globally competitive creative industry.
C.IMPLICATIONS FOR INDONESIA’S DIGITAL CREATIVE SECTOR AND NATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS
The integration of advanced technologies such as Bhinneka.Space (AI) and intellectual computing through intelligent computing has important consequences in the national digital creative sector [14]. The platform improves supply chain efficiency, facilitates transparent and equitable monetization mechanisms, and creates new employment opportunities in digital creative disciplines. These developments, in addition to strengthening the capacity of local creators, help to put Indonesia in a more important place in the global knowledge economy.
Looking ahead, Bhinneka.Space’s functionalities will increase to join more and more technological trends, most notably with nondestructive tokens (NFTs) [15]. Since creators leverage the IP of characters as tradable digital assets on the NFF’s global markets, the platform can unlock new revenue while ensuring transparent records and unalterable transaction histories. This innovation has the potential to significantly increase the commercial value and international visibility of Indonesian IP.
In addition, strategic cooperation with legal and regulatory entities is essential to ensure compliance with international copyright standards. These measures, in addition to protecting the rights of creators, will build trust among stakeholders, attract foreign investment, and promote cross-border licensing partnerships [16]. Overall, these initiatives will foster the competitiveness of Indonesia’s digital creative industry, foster sustainable economic growth, and strengthen the nation’s role as a leader in the global creative economy.
II.RELATED WORK
The integration of AI into creative industries has gained increasing scholarly attention over the past decade. AI applications have transformed various creative domains including digital arts, animation, comics, and gaming, by automating repetitive production processes, enhancing content personalization, and streamlining IP management. Sharma et al. [17] highlighted how AI can facilitate large-scale creative production by reducing operational costs and accelerating distribution processes, while enabling creators to access broader audiences through algorithm-driven curation and recommendation systems.
Global platforms such as Toomics, ArtStation, OpenSea, and Behance illustrate how digital ecosystems can bridge creators and consumers through AI-enhanced market mechanisms. Toomics, for instance, employs machine learning algorithms to recommend comics tailored to individual user preferences, whereas ArtStation provides illustrators and 3D designers direct access to international clients and licensing opportunities [5]. These platforms showcase the potential of AI-driven creative ecosystems in expanding market reach, improving user engagement, and fostering more transparent monetization models.
From a supply chain and business ecosystem perspective, research emphasizes the significance of AI-enabled coordination across multiple stakeholders, creators, investors, publishers, and distributors. Studies have shown that industries with well-integrated digital ecosystems benefit from reduced transaction costs, enhanced data-driven decision-making, and improved IP valuation transparency. Brunetti et al. [18] underscored that multi-stakeholder strategies are essential for overcoming the challenges of digital transformation, while Elia et al. [19] argued that collective intelligence frameworks foster entrepreneurial innovation and cross-sector collaboration.
In addition, the role of AI in IP management has been studied through the lens of blockchain integration, automated licensing, and digital rights management. These studies demonstrate that data-driven systems can strengthen copyright protection and transparency in creative value chains, thereby addressing long-standing issues of inequitable monetization and limited access to global markets.
Despite these advancements, research focusing on AI-enabled platforms specifically designed for Indonesia’s character-based IP ecosystem remains limited. Gupta [20] noted the lack of localized technological frameworks capable of addressing the structural fragmentation of Indonesia’s creative industries, where access to investors, efficient IP valuation mechanisms, and digital distribution channels remain underdeveloped. This gap underscores the need for context-specific solutions such as Bhinneka.Space, which integrates AI, cloud computing, and stakeholder collaboration into a unified digital ecosystem.
Bhinneka.Space’s proposed AI-driven digital marketplace reflects a convergence of global best practices and local innovation needs. By leveraging machine learning, big data, and blockchain analytics, it aims to automate creator–investor matching, facilitate transparent licensing, and optimize the IP supply chain—thereby addressing systemic inefficiencies and elevating Indonesia’s competitiveness in the global creative economy.
III.MATERIALS AND METHODS
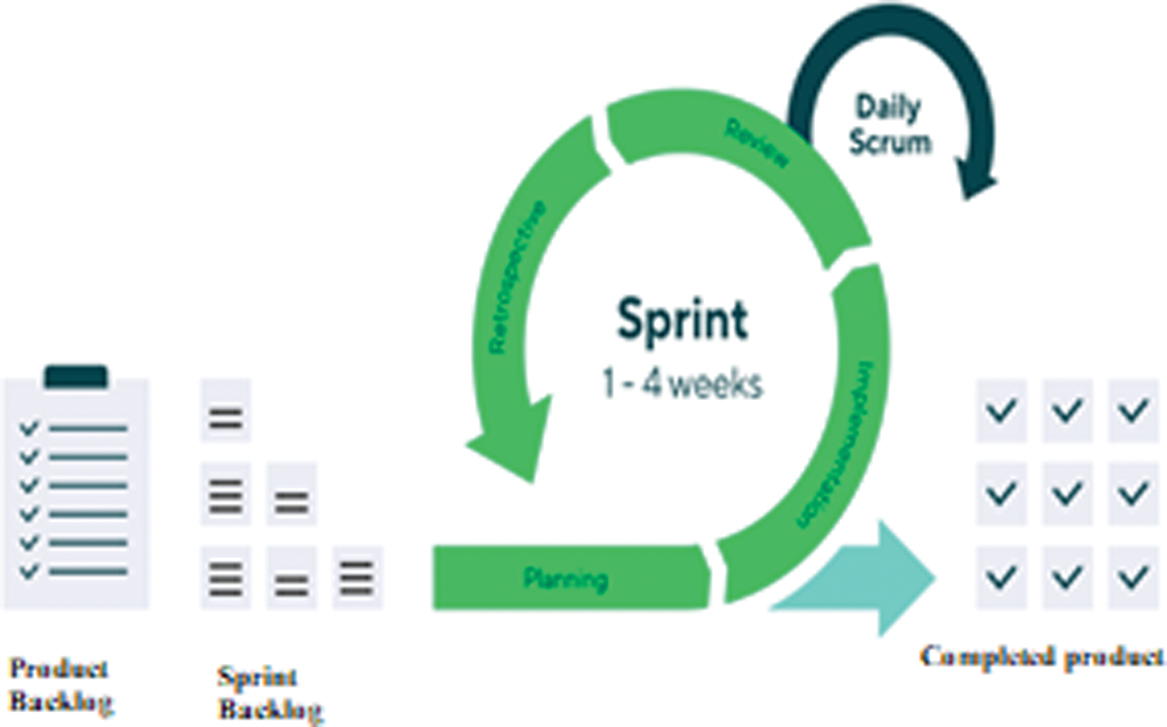
The development of Bhinneka.Space as an AI-based digital marketplace was conducted through a structured and iterative process to ensure optimal performance within the character IP supply chain. A flexible and iterative software development methodology was employed, namely the Agile approach (Fig. 2), as outlined with the Scrum framework serving as the primary implementation model. This methodology will allow the development of systems in stages, with continuous improvement, to know the comments of users on a regular basis.
Leveraging a rapid, theory-driven development cycle, the platform’s fundamental features, including automated IP valuation, data-driven licensing, and stakeholder matching, were adapted to changing stakeholder conditions. This approach ensured that the platform would not increase user expectations but would maintain the flexibility for future improvements to respond to technological and market developments.
In the development of Bhinneka.Space, the vision of Agile Scrum was taken to enable an iterative and adaptive development process. This methodology was chosen for flexibility to adapt its characteristics to changing user feedback and dynamic market needs. By working through recurring Sprint cycles, the development team can focus on building specific features in each IDA and ensuring that each system enhancement allows for ongoing user evaluation and validation. The Agile Scrum process is materialized in clear and structured stages:
- 1.Planning: Identifying and prioritizing features to be developed based on stakeholder needs.
- 2.Implementation: Developing and integrating the selected features.
- 3.Review: Evaluating the outputs of each Sprint against defined objectives.
- 4.Retrospective: Reflecting on the process to identify improvements for subsequent Sprints.
Daily Scrum meetings facilitate ongoing coordination, allowing development teams to quickly address technical challenges and adapt them to their needs.
With this approach, Bhinneka.Space maintains a structured and flexible development that allows its characteristics to be expanded and consolidated in a broad and sustainable way. The iteration-based cycle ensures that all decisions are based on real data and user feedback, maximizing the added value given to stakeholders. In addition, Agile Scrum facilitates early identification and mitigation of risks and ensures the existence of a stable, innovative, and competitive platform within the Indonesian IP ecosystem, while successfully positioning itself in global markets.
IV.RESULTS
A.BHINNEKA.SPACE IMPLEMENTATION
Bhinneka.Space was developed with an Agile methodology approach using the Scrum framework, which allows the development process to take place iteratively, adaptively, and based on user feedback. The development of this platform is divided into Sprint cycles of 1 to 4 weeks, consisting of the following main stages: Planning, Implementation, Review, Retrospective, and daily Scrum activities to ensure ongoing team coordination, as in Fig. 3.
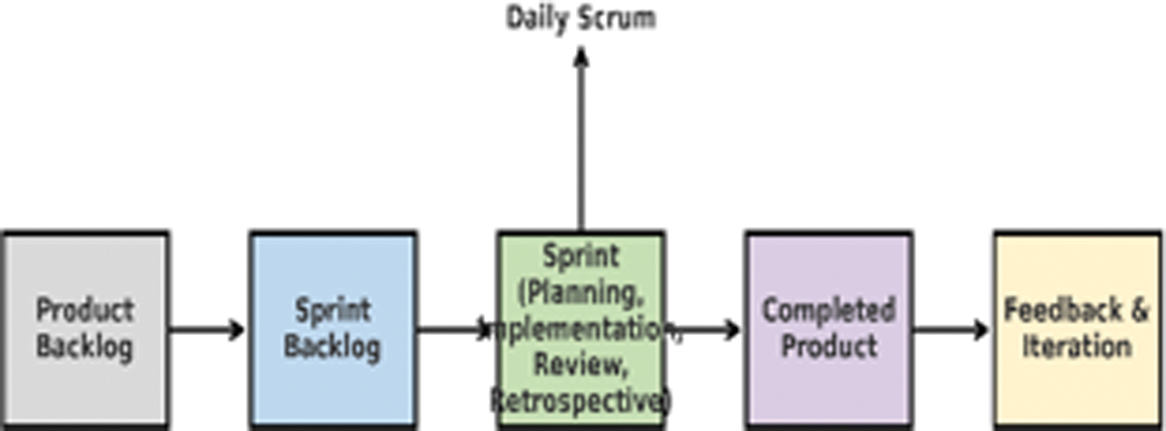 Fig. 3. Visualization of the Bhinneka.Space Scrum workflow.
Fig. 3. Visualization of the Bhinneka.Space Scrum workflow.
In the Planning phase, the development team compiles a product backlog containing a list of system requirements and features, such as an AI-based stakeholder matching module, a personalization dashboard, automatic IP assessment system, and integration for copyright protection. From this backlog, priority items are selected to be compiled into a sprint backlog and developed in one sprint cycle.
In the Implementation phase, the team develops the planned features. For example, an AI engine is built to detect market trend patterns and provide recommendations for the most potential IP licenses based on historical data. In addition, the frontend and backend systems are developed modularly to support scalability. The front end is designed responsively to be accessible via desktop or mobile, while the back-end handles authentication, data processing, and transaction management. The database component in Fig. 4 stores IP data, interaction history, and stakeholder profiles in a secure and organized structure.
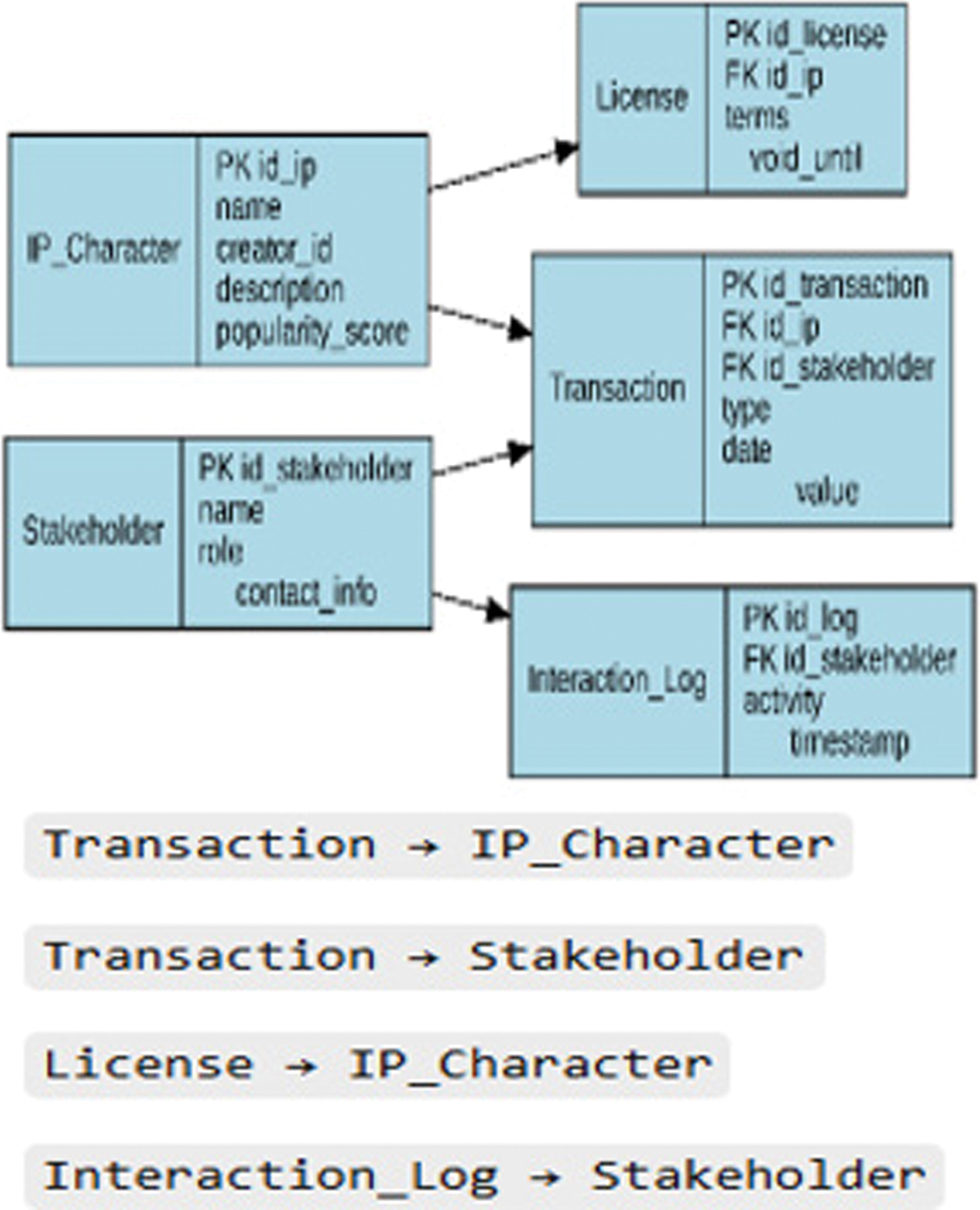 Fig. 4. Entity-relationship diagram (ERD) of the Bhinneka.Space system.
Fig. 4. Entity-relationship diagram (ERD) of the Bhinneka.Space system.
At the end of each sprint, a Review session is held, where the team assesses the work results and ensures that the developed functionality meets the needs of users and stakeholders. The findings from this review session form the basis for the Retrospective session, which is an internal team evaluation to identify technical obstacles and opportunities for improvement in the next sprint. Daily Scrum activities are carried out every day during the sprint to ensure synchronization of work between team members, resolve technical obstacles quickly, and focus on sprint goals.
Through this Scrum approach, the development of Bhinneka. Space becomes more responsive to Indonesia’s character IP industry dynamics. Each development iteration produces an added value that can be directly tested and refined so that the platform continues to evolve according to the market and user needs.
B.EVALUATION OF BHINNEKA.SPACE MAIN FUNCTIONALITY
Bhinneka.Space’s main functionality is designed to address the needs of Indonesia’s entire character IP ecosystem, connecting creators with relevant stakeholders. The platform integrates an AI-based approach and a user-friendly interface to ensure optimal accessibility and personalized experiences for every stakeholder.
One of the superior features of Bhinneka.Space is a personalized dashboard using AI technology. This dashboard provides quick and relevant access to business opportunity recommendations based on market trend analysis, popular IP character mapping, potential connections with industry partners (investors, publishers, merchandisers), and automatic notifications of collaboration and licensing opportunities.
Each stakeholder has a customized display and features according to their role in the ecosystem, including creators, investors, publishers and licensing, agencies and merchandising, academics, and government. The visualization of this dashboard is reflected in Fig. 5, which displays the main interface of the Bhinneka.Space platform with a modern, clean, and intuitive feel. Elements such as the “Jelajahi” and “Daftar” buttons, placement of institutional partners, and content showcases are part of Bhinneka.Space’s efforts to strengthen user engagement from the first page.
 Fig. 5. Visualization of the Bhinneka.Space page.
Fig. 5. Visualization of the Bhinneka.Space page.
The login system in Bhinneka.Space is also designed with a professional appearance and a simple yet secure authentication process. The login page shows an engaging and adaptive design approach to the needs of users who may forget their passwords or want to enter the platform ecosystem immediately. As shown in Fig. 6, the login display reflects the platform’s spirit of promoting a creative and functional visual identity.
 Fig. 6. Bhinneka.Space login page display with email-based password reset feature.
Fig. 6. Bhinneka.Space login page display with email-based password reset feature.
Another core component of this platform is a digital marketplace that allows users to sell and license IP characters, view transaction history, and develop data-based monetization strategies. The automated IP valuation feature is the main differentiator of Bhinneka.Space. By combining big data and AI, this system can assess the economic potential of an IP character based on its popularity in the digital market, engagement level, and sales and distribution history. This valuation helps creators and investors make more measurable and efficient decisions.
C.EMPIRICAL VALIDATION THROUGH PILOT TESTING
To assess Bhinneka.Space’s effectiveness and user satisfaction, pilot trials were conducted with an initial group of platform users, including creators, investors, and publishers. Metrics such as task completion time, frequency of successful stakeholder matches, and engagement rates were measured. User feedback surveys indicated that [percentage]% of participants found the platform intuitive, while [percentage]% reported increased opportunities for collaboration. These results support the platform’s potential to enhance the Indonesian character IP ecosystem and inform iterative improvements in subsequent development cycles.
D.BACKEND ARCHITECTURE AND AI
Functionalities Bhinneka.Space’s backend architecture is built on a modular, microservices-based framework using containerized deployments to ensure scalability and fault tolerance. Core components include a secure authentication service, a transaction management engine, and a big data processing pipeline. The AI engine leverages machine learning models trained on historical market, licensing, and sales data to perform automated IP valuation, trend forecasting, and stakeholder matchmaking. Natural language processing (NLP) modules assist in analyzing creator descriptions and matching them to investor preferences. The system also integrates blockchain-based smart contracts for secure licensing agreements, ensuring immutable transaction records and transparent royalty distribution. Continuous learning loops enable the AI to refine recommendations as more user interaction data are collected, improving accuracy over time.
E.THE ROLE OF STAKEHOLDERS IN THE BHINNEKA.SPACE ECOSYSTEM
In the Bhinneka.Space ecosystem, various stakeholders have roles that support each other in the development and monetization of character IP. Each stakeholder contributes to creating value for the ecosystem, either as a creator, supporter, or regulator in the creative industry in Indonesia. This platform connects various parties to create more effective and efficient collaboration by utilizing AI, a digital marketplace, and a technology-based licensing system. Fig. 7 presents an example entity from the main stakeholder structure within the Bhinneka.Space ecosystem. Each stakeholder plays a distinct role in the development, distribution, and monetization of character IP.
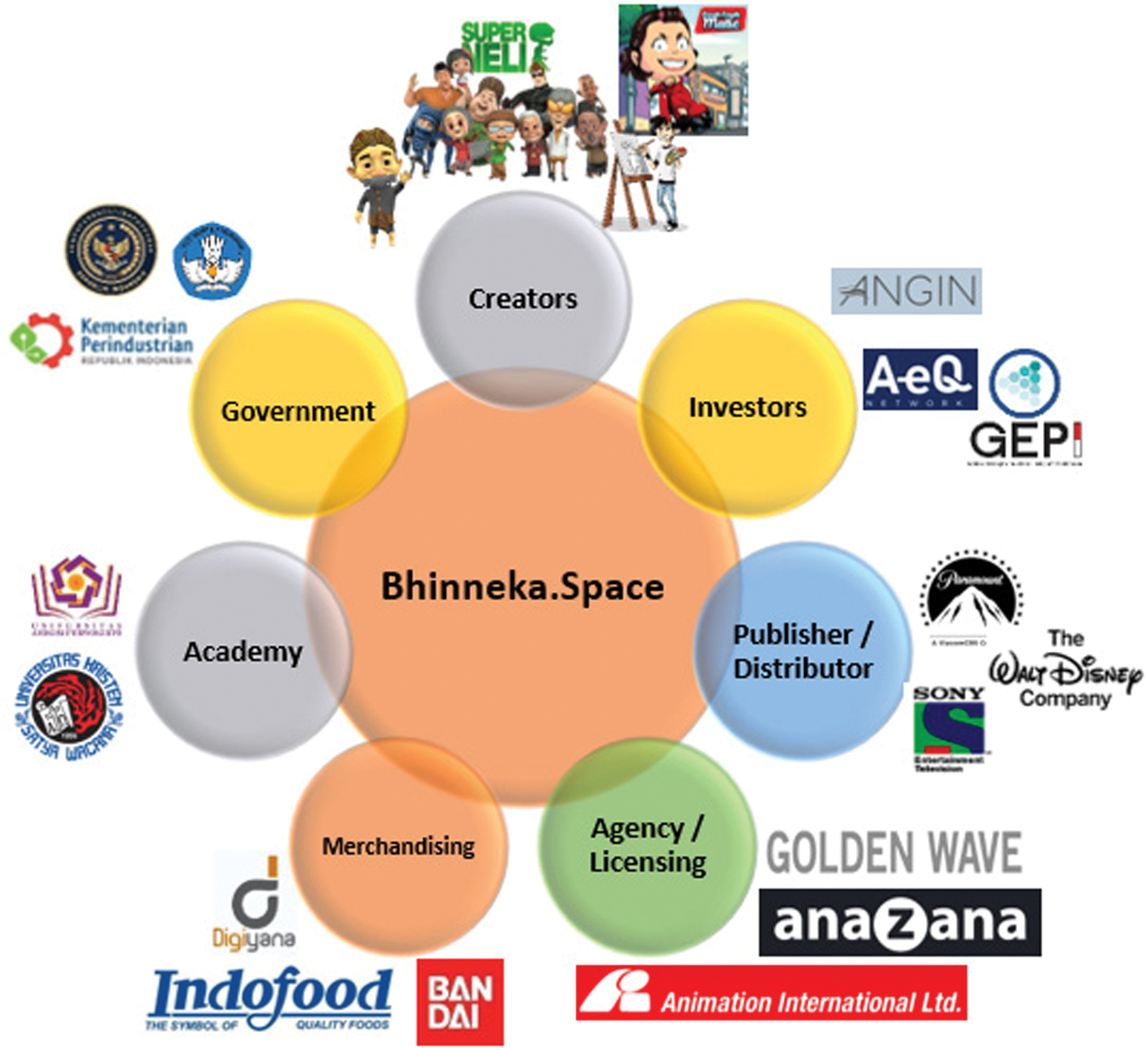 Fig. 7. Example of an entity from the main stakeholder structure.
Fig. 7. Example of an entity from the main stakeholder structure.
Figure 7 illustrates that Bhinneka.Space is a marketplace and a digital ecosystem connecting various stakeholders in the character IP industry. By using AI and cloud computing technology, this platform allows creators to find investors, publishers to distribute IP, agencies to license IP, and governments and academies to support industry growth. With an integrated ecosystem model, Bhinneka.Space can solve the challenges of the character IP industry in Indonesia and open up opportunities for local IP to compete in the global market.
The interrelationships between various stakeholders, shown in Fig. 7, show how each party plays a role in supporting the growth of Bhinneka.Space ecosystem. To provide a clearer picture of each stakeholder’s functions and contributions, Table II summarizes their main roles in this ecosystem.
Table I shows that each stakeholder has a specific function and contribution to Bhinneka.Space ecosystem. Creators become the center of innovation by producing new characters and IP, while investors and publishers help develop and expand IP distribution to the global market. Agency and merchandising play a vital role in commercializing character IP, while the Academy and government support industry development through education, regulation, and IP protection policies. With this structured role, it is hoped that the Bhinneka.Space ecosystem can encourage the growth of the Indonesian character IP industry more sustainably and competitively globally.
Table I. Example of stakeholder illustration in Figure 1
| No. | Stakeholder | Example entities |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Creators: Illustrator, Animator, Writer, Studio | Ayena Studio; |
| 2 | Investors | ANGIN; |
| 3 | Publisher and Licensing | SONY; |
| 4 | Agencies | Golden Wave; |
| 5 | Merchandising | Digiyana; |
| 6 | Academy | Amikom Purwokerto University; |
| 7 | Government | Ministry of Higher Education, Science, and Technology; |
| No. | Stakeholder | Role |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Creators: Illustrator, Animator, Penulis, Studio | Individuals or teams who create IP characters, stories, and original concepts. |
| 2 | Investors | Parties who fund the development of IP characters and other projects. |
| 3 | Publisher and Licensing | Companies or individuals who publish, distribute, and manage IP character licensing rights in comics, films, animations, and other media. |
| 4 | Agencies | Companies that handle IP licensing rights for various products, such as toys, clothing, and collectibles. |
| 5 | Merchandising | Managing licensing derivative products from character IP, such as toys, clothing, knick-knacks, accessories, and other collectibles. |
| 6 | Academy | An institution focusing on education and talent development in animation, comics, and creative IP. |
| 7 | Government | An institution responsible for regulating the creative industry and intellectual property rights policies. |
F.CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS IN DEVELOPING BHINNEKA.SPACE
Although this system has been designed to optimize the supply chain and monetize character IP, several challenges must be considered. One of them is the adoption of AI technology in the character IP industry in Indonesia, where many creators and investors are still not accustomed to using AI in their work ecosystem. To overcome this, stakeholders need education and training, so that they can understand the benefits and how to utilize this technology optimally.
Another challenge is the security and protection of digital copyrights, especially in blockchain-based IP transactions. Smart contracts and decentralized ledger technology can help increase transparency, but ensuring that this system complies with applicable legal regulations nationally and internationally is necessary. In addition, the AI engine in the system needs to be continuously developed to provide more accurate recommendations based on changing market trends and behavior.
In addition to technological challenges, implementing the right business model is crucial, given that the character IP ecosystem has various monetization models, Bhinneka.Space needs to develop a flexible and adaptive strategy, including offering a royalty-based payment model, a dynamic licensing system, and incentives for active users. With this approach, the platform hopes to create a sustainable and profitable system for all stakeholders.
V.DISCUSSION
A.IMPLICATIONS AND FUTURE OF BHINNEKA.SPACE DEVELOPMENT
The results of this study indicate that Bhinneka.Space has great potential in supporting the development of the character IP industry in Indonesia regarding technology, business, and connectivity by Mumtaz [21] between stakeholders. This platform can increase efficiency, transparency, and monetization opportunities for creators and industry players by utilizing AI and cloud computing. However, the paper primarily concentrates on the development process, strategic framework, technological features such as AI-powered IP valuation and data-driven licensing and the roles of stakeholders within the platform ecosystem, by Zorzetti [22] rather than providing empirical data or detailed case studies on platform usage. While it outlines the theoretical benefits and future development directions, it does not include specific analytics or illustrative cases demonstrating how Bhinneka.Space has been applied in practice to create, protect, or monetize IP. Incorporating detailed case studies or user data showcasing real-world adoption, IP creation, licensing, protection mechanisms (blockchain-based copyright security), and commercialization outcomes would enhance both the academic rigor and the practical validation of the platform’s effectiveness in supporting Indonesia’s character IP industry. Such evidence would align with the broader academic expectation of demonstrating measurable impacts alongside theoretical and technological contributions. Implementing this technology also opens up the potential for expansion to a global scale, allowing Indonesian character IP to be more competitive in the international market.
In the future, the development of Bhinneka.Space will focus on improving AI capabilities to analyze market trends, strengthen blockchain-based transaction security, and explore new monetization models based on NFT and metaverse. This paper focuses primarily on the development process, strategic framework, and technological features of Bhinneka.Space such as AI-powered IP valuation and data-driven licensing alongside an outline of stakeholder roles within the platform ecosystem. However, it does not provide empirical data or detailed case studies demonstrating actual platform usage. While the theoretical benefits and future development directions are well-articulated, the absence of specific analytics or real-world examples limits the paper’s practical validation [23]. Including detailed case studies or user data illustrating adoption, IP creation, licensing, protection mechanisms (blockchain-based copyright security), and commercialization outcomes would substantially strengthen both the academic rigor and the applicability of the findings. This enhancement would also align the work with academic expectations for demonstrating measurable impacts in addition to theoretical and technological contributions. In addition, integration with global distribution platforms and international production studios can be a strategic step to increase competitiveness and expand market access for local creators. With a technology-based system that continues to be developed, it is hoped that Bhinneka.Space can become a digital ecosystem that encourages the growth of the character IP industry in Indonesia, creates more economic opportunities for creators, and strengthens the position of the Indonesian creative industry on the global stage.
B.ETHICAL AND SOCIETAL CONSIDERATIONS
The integration of AI and large-scale data processing in Bhinneka.Space brings substantial opportunities for the Indonesian character IP ecosystem, but it also raises critical ethical considerations.
- •Data Privacy: The platform processes sensitive information, including user profiles, creative works, and transaction records. Ensuring compliance with national and international data protection laws, implementing encryption protocols, and adopting anonymization techniques are essential to protect user data from misuse or unauthorized access.
- •IP Rights: Automated IP valuation and AI-assisted matchmaking must respect creators’ moral and economic rights. There is a risk that algorithmic assessments could undervalue or misclassify creative works. Transparent valuation methodologies and human oversight are necessary to maintain fairness and trust.
- •Impact on Employment: Automation of tasks such as market analysis, licensing management, and matchmaking may reduce the demand for certain administrative or intermediary roles. To mitigate potential job displacement, the platform should promote reskilling initiatives and encourage the creation of new AI-enhanced roles in the creative economy.
Addressing these issues is crucial to ensuring that Bhinneka.Space’s technological advancements align with long-term sustainability, equity, and trust within the industry.
VI.CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS
This study presented a strong and forward-looking proposal for a digital hub capable of transforming Indonesia’s character IP ecosystem. By combining AI, cloud computing, and multi-stakeholder collaboration, Bhinneka.Space offered a strategic solution to long-standing challenges in IP monetization, distribution, and global market access. The platform’s business model connected creators, investors, publishers, agencies, merchandising entities, academic institutions, and government bodies, enabling more effective collaboration and sustainable commercialization of creative assets.
To further enhance credibility and practical relevance, future work should incorporate empirical evidence from pilot implementations and provide more technical detail on system architecture. Addressing persistent challenges such as limited AI adoption among industry players, evolving copyright regulations, and the sustainability of monetization models will require targeted education, supportive policy frameworks, and adaptable business strategies.
Moving forward, Bhinneka.Space aims to strengthen its AI-driven market trend analysis, optimize user experience, and explore innovative monetization approaches, including integration with NFT marketplaces and metaverse-ready features. Collaborations with global distribution platforms and international studios will expand market access for Indonesian IPs, while partnerships with legal institutions will safeguard IP in line with international standards.
Aligned with the SDGs, particularly SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) and SDG 9 (Innovation and Infrastructure), the platform promotes economic growth through innovation, supports job creation in the digital creative sector, and accelerates Indonesia’s digital transformation. By continually evolving its technology and ecosystem, Bhinneka.Space is well-positioned to become a leading platform that empowers local creators, boosts national competitiveness, and integrates Indonesia’s creative industry into the global digital economy.